Optimal control of blood glucose: the diabetic patient or the machine?
- PMID: 20393187
- PMCID: PMC4620569
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001083
Optimal control of blood glucose: the diabetic patient or the machine?
Abstract
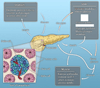
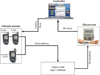
In this issue of Science Translational Medicine, El-Khatib et al. describe a "closed-loop" bihormonal artificial pancreas, designed to avert episodes of low blood sugar in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. We discuss the benefits and challenges of therapy directed at tight control of blood glucose and ask whether this and similar technological breakthroughs can address as yet unanswered questions in the biology of diabetes.
Figures
Comment on
-
A bihormonal closed-loop artificial pancreas for type 1 diabetes.Sci Transl Med. 2010 Apr 14;2(27):27ra27. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000619. Sci Transl Med. 2010. PMID: 20393188 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Joslin EP. Diabetic Manual for the Mutual Use of Doctor and Patient. ed. 5th. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febiger; 1933. The treatment of diabetes with diet and exercise; pp. 100–120.
-
- Joslin EP. A Diabetic Manual for the Mutual Use of Doctor and Patient. ed. 1st. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febinger; 1918.
-
- Cryer PE, Gerich JE. Glucose counterregulation, hypoglycemia, and intensive insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus. N Engl. J. Med. 1985;313:232–241. - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N/ Engl. J. Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed
-
- Palmer AJ, Roze S, Valentine WJ, Minshall ME, Lammert M, Nicklasson L, Spinas GA. Deleterious effects of increased body weight associated with intensive insulin therapy for type 1 diabetes: increased blood pressure and worsened lipid profile partially negate improvements in life expectancy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004;20(Suppl 1):S67–S73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

