Cisapride treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children
- PMID: 20393933
- PMCID: PMC7138252
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300.pub2
Cisapride treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children
Abstract
Background: Gastro-oesophageal reflux (GOR) is common and usually self-limiting in infants. Cisapride, a pro-kinetic agent, was commonly prescribed until reports of possible serious adverse events were associated with its use.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness of cisapride versus placebo or non-surgical treatments for symptoms of GOR.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Group Specialised Register and Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE and EMBASE, reference lists of relevant review articles and searched in the Science Citation Index for all the trials identified. All searches were updated in February 2009.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials comparing oral cisapride therapy with placebo or other non-surgical treatments for children diagnosed with GOR were included. We excluded trials with a majority of participants less than 28 days of age.
Data collection and analysis: Primary outcomes were a change in symptoms at the end of treatment, presence of adverse events, occurrence of clinical complications and weight gain. Secondary outcomes included physiological measures of GOR or histological evidence of oesophagitis. We dichotomised symptoms into 'same or worse' versus 'improved' and calculated summary odds ratios (OR). Continuous measures of GOR (for example reflux index) were summarised as a weighted mean difference. All outcomes were analysed using a random-effects method.
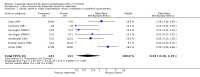
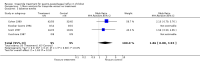
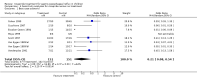
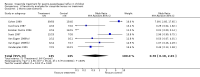
Main results: Ten trials in total met the inclusion criteria. Nine trials compared cisapride with placebo or no treatment, of which eight (262 participants) reported data on symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux. There was no statistically significant difference between the two interventions (OR 0.34; 95% CI 0.10 to 1.19) for 'same or worse' versus 'improved symptoms' at the end of treatment. There was significant heterogeneity between the studies, suggesting publication bias. Four studies reported adverse events (mainly diarrhoea); this difference was not statistically significant (OR 1.80; 95% CI 0.87 to 3.70). Another trial found no difference in the electrocardiographic QTc interval after three to eight weeks of treatment. Cisapride significantly reduced the reflux index (weighted mean difference -6.49; 95% CI -10.13 to -2.85; P = 0.0005). Other measures of oesophageal pH monitoring did not reach significance. One included study compared cisapride with Gaviscon (with no statistically significant difference). One small study found no evidence of benefit on frequency of regurgitation or weight gain after treatment with cisapride versus no treatment, carob bean or corn syrup thickeners.
Authors' conclusions: We found no clear evidence that cisapride reduces symptoms of GOR. Due to reports of fatal cardiac arrhythmias or sudden death, from July 2000 in the USA and Europe cisapride was restricted to a limited access programme supervised by a paediatric gastrologist.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures









Update of
-
Cisapride treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Apr 14;(4):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300.pub2. PMID: 14583950 Updated.
Similar articles
-
Cisapride treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Apr 14;(4):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300.pub2. PMID: 14583950 Updated.
-
Cisapride treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300. PMID: 12137654 Updated.
-
Cisapride treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(3):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD002300. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002300. PMID: 10908549 Updated.
-
Pharmacological treatment of children with gastro-oesophageal reflux.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 24;2014(11):CD008550. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008550.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 22;8:CD008550. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008550.pub3. PMID: 25419906 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Pharmacological treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Aug 22;8(8):CD008550. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008550.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37635269 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gastro-esophageal reflux: spitting and possetting in a neonate.Indian J Pediatr. 2015 Jan;82(1):39-43. doi: 10.1007/s12098-014-1535-z. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Indian J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25109680 Review.
-
Targeting 5-HT Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 15;25(24):13446. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413446. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease in neonates and infants : when and how to treat.Paediatr Drugs. 2013 Feb;15(1):19-27. doi: 10.1007/s40272-012-0004-2. Paediatr Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23322552 Review.
-
Developmental changes in the expression and function of cytochrome P450 3A isoforms: evidence from in vitro and in vivo investigations.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 May;52(5):333-45. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0041-1. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23463352 Review.
-
Medical management of gastro-esophageal reflux in healthy infants.Paediatr Child Health. 2022 Dec 27;27(8):503-511. doi: 10.1093/pch/pxac068. eCollection 2022 Dec. Paediatr Child Health. 2022. PMID: 36583075 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
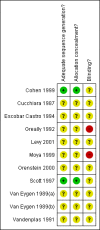
Cohen 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cohen RC, O'Loughlin EV, Davidson GP, Moore DJ, Lawrence DM. Cisapride in the control of symptoms in infants with gastroesophageal reflux. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Pediatrics 1999;134:287‐92. - PubMed
-
- Davidson GP. Personal communication [Clarification of trial characteristics and additional data]. Meeting 14.09.99.
Cucchiara 1987 {published data only}
Escobar Castro 1994 {published data only}
-
- Escobar Castro H, Bettas Ferrero G, Suarez Cortina L, Camarero Salces C, Lima M. Efficacy of cisapride in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux (GER) in children. Evaluation of a double blind study [Efectividad del Cisapride en el tratamiento del reflujo gastroesofagico (R.G.E.) en ninos. Valoracion de un estudio a doble ciego]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1994;40(1):5‐8.
Greally 1992 {published data only}
Levy 2001 {published data only}
-
- Levy J, Hayes C, Kern J, Harris J, Flores A, Hyams J, et al. Does cisapride influence cardiac rhythm? Results of a United States multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled pediatric study. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2001;32:458‐63. - PubMed
Moya 1999 {published data only}
-
- Moya M, Juste M, Cortes E, Auxina A, Ortiz L. Clinical evaluation of the different therapeutic possibilities in the treatment of infant regurgitation. [Valoracion clinica de las distintas posibilidades terapeuticas en el manejo de las regurgitaciones del lactante]. Revista Espanola de Pediatria 1999;55(3):219‐23.
Orenstein 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Orenstein SR. Personal communication [Additional data and details regarding completion of the study]. Email 11.06.09.
-
- Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Frankel EA, Kelsey SF. Cisapride, cimetidine, both or neither for infantile esophagitis: symptomatic and histologic results of 2‐months randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled therapy in 100 babies. Gastroenterology 2000;118(4):A20.
-
- Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Kelsey SF, Frankel E. Natural history of infant reflux esophagitis: symptoms and morphometric histology during one year without pharmacotherapy. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2006;101(3):628. - PubMed
-
- Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Kelsey SF, Frankel EA. Cimetidine, cisapride, both or neither for infant esophagitis: symptomatic response to 6m randomized, double blind, placebo‐controlled therapy in 100 babies. Gastroenterology 2004;126 Suppl 2(4):A508.
-
- Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Kelsey SF, Frankel EA. Cimetidine, cisapride, both or neither for infantile esophagitis: symptomatic response to 4m randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled therapy in 100 babies [Abstracts: Poster session abstracts]. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2004;39 Suppl 1:P0791.
Scott 1997 {published data only}
-
- Scott RB, Ferreira C, Smith L, Jones AB, Machida H, Lohoues MJ, et al. Cisapride in pediatric gastroesophageal reflux. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1997;25:499‐506. - PubMed
Van Eygen 1989(a) {published data only}
-
- Eygen M, Ravensteyn H. Effect of cisapride on excessive regurgitation in infants. Clinical Therapeutics 1989;11(5):669‐77. - PubMed
Van Eygen 1989(b) {published data only}
-
- Eygen M, Ravensteyn H. Effect of cisapride on excessive regurgitation in infants. Clinical Therapeutics 1989;11(5):669‐77. - PubMed
Vandenplas 1991 {published data only}
-
- Vandenplas Y, Roy C, Sacre L. Cisapride decreases prolonged episodes of reflux in infants. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1991;12:44‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Barnett 2001 {published data only}
-
- Barnett CP, Omari T, Davidson GP, Goodchild L, Lontis R, Dent J, et al. Effect of cisapride on gastric emptying in premature infants with feed intolerance. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2001;37:559‐63. - PubMed
Cucchiara 1990 {published data only}
Enriquez 1998 {published data only}
Heine 1996 {published data only}
-
- Heine RG, Catto‐Smith AG, Reddihough DS. Effect of antireflux medication on salivary drooling in children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1996;38:1030‐6. - PubMed
McClure 1999 {published data only}
Pezzati 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pezzati M, Dani C, Biadaioli R, Gambi B, Lachina L, Rubaltelli FF. Randomised controlled trial of the effect of cisapride on the pyloric muscle in preterm infants. European Journal of Pediatrics 2001;160:572‐5. - PubMed
Reddy 2000 {published data only}
-
- Reddy PS, Deorari AK, Bal CS, Paul VK, Singh M. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled study on prophylactic use of cisapride on feed intolerance and gastric emptying in preterm neonates. Indian Pediatrics 2000;37:837‐44. - PubMed
Saye 1987 {published data only}
-
- Saye ZN, Forget P, Geubelle F. Effect of Cisapride on gastroesophageal reflux in children with chronic bronchopulmonary disease: A double‐blind cross‐over pH‐monitoring study. Pediatric Pulmonology 1987;3:8‐12. - PubMed
Additional references
Breckenridge 2000
-
- Breckenridge A. Suspension of cisapride (Prepulsid) licences: Product withdrawal. Committee on Safety of Medicines, London 2000.
Colson 1990
Cucchiara 1996
-
- Cucchiara S, Campanozzi A, Greco L, Franco MT, Emiliano M, Alfieri E, et al. Predictive value of esophageal manometry and gastroesophageal pH monitoring for responsiveness of reflux disease to medical therapy in children. American Journal of Gastroeneterology 1996;91(4):680‐5. - PubMed
Davidson 2009
-
- Davidson GP. Personal communication [Clarification of trial characteristics and additional data]. Meeting 14.9.99.
Egger 1997
EMEA 2002
-
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for proprietary medicinal products (CPMP) opinion following and article 31 referral. Cisapride. EMEA/CPMP/24844/02. http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/referral/cisapride/2484402en.pdf London 7 October 2002. Accessed 26/01/10.
Hampton 1990
Henney 2000
-
- Henney JE. Withdrawal of troglitazone and cisapride. JAMA 2000;283:2228. - PubMed
Higgins 2009
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Klausner 1998
-
- Klausner MA. Jansen Pharmaceutical Research Foundation. Important safety and efficacy information. http://pharminfo.com/medwatch/mwrpt50.html (accessed June 2000) 1998.
Nelson 1997
-
- Nelson SP, Chen EH, Syniar GM, Kaufer Christoffel K. Prevalence of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux during infancy. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 1997;151:569‐72. - PubMed
Orenstein 2009
-
- Orenstein SR. Personal communication [Additional data and details regarding completion of the study]. Email 11.06.09.
Rudolph 1996
-
- Rudolph CD. Gastroesophageal Reflux. In: Rudolph AM, Hoffman JIE, Rudolph CD editor(s). Rudolph's Pediatrics. Stamford, Connecticut: Appleton and Lange, 1996:1058‐60.
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Shulman 2000
-
- Shulman RJ, Boyle JT, Colletti RB, Friedman R, Heyman MB, Kearns G, et al. The North American Society for Pediatrics Gastroenterology and Nutrition. An updated medical position statement of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2000;31(2):232‐3. - PubMed
Treem 1991
-
- Treem WR, Davis PM, Hyams JS. Gastroesophageal reflux in the older child: presentation, response to treatment and long‐term follow‐up. Clinical Pediatrics 1991;30(7):435‐40. - PubMed
Vandenplas 1993
-
- Vandenplas Y, Ashkenazi A, Belli D, Boige N, Bouquet J, Cadranel S, et al. A proposition for the diagnosis and treatment of gastro‐oesophageal reflux disease in children: a report from a working group on gastro‐oesophageal reflux disease. European Journal of Pediatrics 1993;152:704‐11. - PubMed
Vandenplas 1999
-
- Vandenplas Y, Belli DC, Benatar A. The role of cisapride in the treatment of pediatric gastroesophageal reflux. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1999;28:518‐28. - PubMed
Varty 1993
Ward 1999
-
- Ward RM, Lemons JA, Molteni RA. Cisapride: a survey of the frequency of use and adverse events in premature newborns. Pediatrics 1999;103:469‐72. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Gilbert RE et al
-
- Gilbert RE, Augood C, MacLennan S, Logan S. Cisapride treatment for gastro‐oesophageal reflux: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2000;36:525‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

