Triptans for acute cluster headache
- PMID: 20393964
- PMCID: PMC4170909
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008042.pub2
Triptans for acute cluster headache
Update in
-
Triptans for acute cluster headache.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 17;2013(7):CD008042. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008042.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24353996 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Cluster headache is an uncommon, but severely painful and disabling condition, with rapid onset. Validated treatment options are limited, and first-line therapy includes inhaled oxygen. Alternative therapies such as intranasal lignocaine and ergotamine are not as commonly used and are less well studied. Triptans are successfully used to treat migraine attacks and, because of this, they may also be useful for cluster headache.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy and tolerability of triptans for the acute treatment of cluster headaches.
Search strategy: We searched Cochrane CENTRAL, MEDLINE and EMBASE for studies through 22 January 2010.
Selection criteria: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of triptans for acute treatment of cluster headache episodes.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed study quality and extracted data. Numbers of participants with different levels of pain relief, requiring rescue medication and experiencing adverse events and headache-associated symptoms in treatment and control groups were used to calculate relative risk and numbers needed to treat (NNT) and harm (NNH).
Main results: All six included studies used a single dose of triptan to treat an attack of moderate to severe pain intensity. In total 231 participants received zolmitriptan 5 mg, 223 received zolmitriptan 10 mg, 131 received sumatriptan 6 mg, 88 received sumatriptan 12 mg, and 326 received placebo. Zolmitriptan was administered either orally or intranasally, and sumatriptan either subcutaneously or intranasally.Overall, the triptans studied were better than placebo for headache relief and pain-free responses, with an NNT of 2.4 for 15 minute pain relief with subcutaneous sumatriptan 6 mg (75% with sumatriptan and 32% with placebo), and 2.8 for 30 minute pain relief with intranasal zolmitriptan 10 mg (62% with zolmitriptan and 26% with placebo). Fewer participants need rescue medication with triptan than with placebo, but more experienced adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: Zolmitriptan and sumatriptan are effective in the acute treatment of cluster headaches and may provide a useful treatment option, potentially offering convenience over oxygen therapy and a better safety and tolerability profile than ergotamine. Non-oral routes of administration are likely to provide better and more rapid responses.
Figures

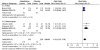

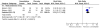

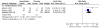
Comment in
-
Evidence-based emergency medicine. Do triptans effectively treat acute cluster headache in the emergency department?Ann Emerg Med. 2011 Sep;58(3):284-5. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2011.02.013. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Ann Emerg Med. 2011. PMID: 21396737 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
-
- Bahra A, Gawel MJ, Hardebo JE, Millson D, Breen SA, Goadsby PJ. Oral zolmitriptan is effective in the acute treatment of cluster headache. Neurology. 2000;54(9):1832–9. - PubMed
-
- Cittadini E, May A, Straube A, Evers S, Bussone G, Goadsby PJ. Effectiveness of intranasal zolmitriptan in acute cluster headache: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover study. Archives of Neurology. 2006;63(11):1537–42. DOI: 10.1001/archneur.63.11.nct60002. - PubMed
-
- The Sumatriptan Cluster Headache Study Group Treatment of acute cluster headache with sumatriptan. New England Journal of Medicine. 1991;325(5):322–6. - PubMed
-
- Ekbom K, Monstad I, Prusinski A, Cole JA, Pilgrim AJ, Noronha D, The Sumatriptan Cluster Headache Study Group Subcutaneous sumatriptan in the acute treatment of cluster headache: a dose comparison study. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 1993;88(1):63–9. - PubMed
-
- Rapoport AM, Mathew NT, Silberstein SD, Dodick D, Tepper SJ, Sheftell FD, et al. Zolmitriptan nasal spray in the acute treatment of cluster headache: a double-blind study. Neurology. 2007;69(9):821–6. DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000267886.85210.37. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
-
- Bennett MH, French C, Schnabel A, Wasiak J, Kranke P. Normobaric and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for migraine and cluster headache. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2008;(3) DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005219.pub2. - PubMed
-
- The Sumatriptan Cluster Headache Study Group Treatment of acute cluster headache with sumatriptan. New England Journal of Medicine. 1991;325(5):322–6. - PubMed
-
- D’Alessandro R, Gamberini G, Benassi G, Morganti G, Cortelli Lugaresi E. Cluster headache in the Republic of San Marino. Cephalalgia. 1986;6(3):159–62. - PubMed
-
- Dodick DW, Martin VT, Smith T, Silberstein S. Cardiovascular tolerability and safety of triptans: a review of clinical data. Headache. 2004;44(Suppl 1):S20–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

