Chronic caffeine treatment prevents sleep deprivation-induced impairment of cognitive function and synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 20394312
- PMCID: PMC2849782
- DOI: 10.1093/sleep/33.4.437
Chronic caffeine treatment prevents sleep deprivation-induced impairment of cognitive function and synaptic plasticity
Abstract
Study objectives: This study was undertaken to provide a detailed account of the effect of chronic treatment with a small dose of caffeine on the deleterious effects of sleep loss on brain function in rats.
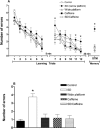
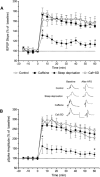
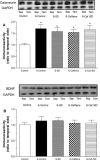
Experimental design: We investigated the effects of chronic (4 weeks) caffeine treatment (0.3 g/L in drinking water) on memory impairment in acutely (24 h) sleep-deprived adult male Wistar rats. Sleep deprivation was induced using the modified multiple platform model. The effects of caffeine on sleep deprivation-induced hippocampus-dependent learning and memory deficits were studied by 3 approaches: learning and memory performance in the radial arm water maze task, electrophysiological recording of early long-term potentiation (E-LTP) in area CA1 of the hippocampus, and levels of memory- and synaptic plasticity-related signaling molecules after E-LTP induction.
Measurement and results: The results showed that chronic caffeine treatment prevented impairment of hippocampus-dependent learning, shortterm memory and E-LTP of area CA1 in the sleep-deprived rats. In correlation, chronic caffeine treatment prevented sleep deprivation-associated decrease in the levels of phosphorylated calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (P-CaMKII) during expression of E-LTP.
Conclusions: The results suggest that long-term use of a low dose of caffeine prevents impairment of short-term memory and E-LTP in acutely sleep-deprived rats.
Figures

References
-
- Blissitt PA. Sleep, memory, and learning. J Neurosci Nurs. 2001;33:208–15. - PubMed
-
- Polzella DJ. Effects of sleep deprivation on short-term recognition memory. J Exp Psychol [Hum Learn] 1975;104:194–200. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara M, Iaria G, Tempesta D, et al. Sleep to find your way: the role of sleep in the consolidation of memory for navigation in humans. Hippocampus. 2008;18:844–51. - PubMed
-
- Kim EY, Mahmoud GS, Grover LM. REM sleep deprivation inhibits LTP in vivo in area CA1 of rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 2005;388:163–7. - PubMed
-
- Forest G, Godbout R. Effects of sleep deprivation on performance and EEG spectral analysis in young adults. Brain Cogn. 2000;43:195–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

