A mutation affecting the sodium/proton exchanger, SLC9A6, causes mental retardation with tau deposition
- PMID: 20395263
- PMCID: PMC2859154
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awq071
A mutation affecting the sodium/proton exchanger, SLC9A6, causes mental retardation with tau deposition
Abstract
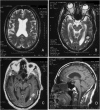
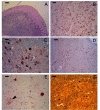
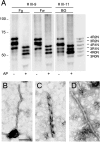
We have studied a family with severe mental retardation characterized by the virtual absence of speech, autism spectrum disorder, epilepsy, late-onset ataxia, weakness and dystonia. Post-mortem examination of two males revealed widespread neuronal loss, with the most striking finding being neuronal and glial tau deposition in a pattern reminiscent of corticobasal degeneration. Electron microscopic examination of isolated tau filaments demonstrated paired helical filaments and ribbon-like structures. Biochemical studies of tau demonstrated a preponderance of 4R tau isoforms. The phenotype was linked to Xq26.3, and further analysis identified an in-frame 9 base pair deletion in the solute carrier family 9, isoform A6 (SLC9A6 gene), which encodes sodium/hydrogen exchanger-6 localized to endosomal vesicles. Sodium/hydrogen exchanger-6 is thought to participate in the targeting of intracellular vesicles and may be involved in recycling synaptic vesicles. The striking tau deposition in our subjects reveals a probable interaction between sodium/proton exchangers and cytoskeletal elements involved in vesicular transport, and raises the possibility that abnormalities of vesicular targeting may play an important role in more common disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and autism spectrum disorders.
Figures
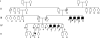
References
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351:602–11. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Shikamoto Y, Tsuchiya K, Yagishita S, et al. Distinct isoforms of tau aggregated in neurons and glial cells in brains of patients with Pick’s disease, corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol. 2001;101:167–73. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DD. Neuropathology of Rett syndrome. J Child Neurol. 2005;20:747–53. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong RA, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL. A quantitative study of the pathological lesions in the neocortex and hippocampus of twelve patients with corticobasal degeneration. Exp Neurol. 2000;163:348–56. - PubMed
-
- Belfor N, Amici S, Boxer AL, Kramer JH, Gorno-Tempini ML, Rosen HJ, et al. Clinical and neuropsychological features of corticobasal degeneration. Mech Ageing Dev. 2006;127:203–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

