Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and NF-E2-related factor 2 are key regulators of human MRP4 expression
- PMID: 20395535
- PMCID: PMC2904108
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00522.2010
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and NF-E2-related factor 2 are key regulators of human MRP4 expression
Abstract
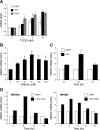
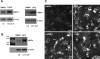
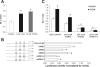
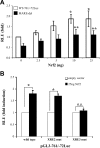
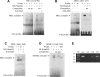
Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4; ABCC4) is an ATP binding cassette transporter that facilitates the excretion of bile salt conjugates and other conjugated steroids in hepatocytes and renal proximal tubule epithelium. MRP4/Mrp4 undergoes adaptive upregulation in response to oxidative and cholestatic liver injury in human and animal models of cholestasis. However, the molecular mechanism of this regulation remains to be determined. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) play important roles in protecting cells from oxidative stress. Here we examine the role of these two nuclear factors in the regulation of the expression of human MRP4. HepG2 cells and human hepatocytes were treated with the AhR and Nrf2 activators, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MC), or oltipraz and other nuclear receptor agonists. TCDD, 3-MC, and oltipraz significantly increased MRP4 expression at mRNA and protein levels. Computer program analysis revealed three Xenobiotic response element (XRE) and one Maf response element sites within the first 500 bp of the MRP4 proximal promoter. Luciferase reporter assay detected strong promoter activity (53-fold higher than vector control) in this region. TCDD and 3-MC also induced promoter activity in the reporter assays. Mutation of any of these XRE sites significantly decreased MRP4 promoter activity in reporter assays, although XRE2 demonstrated the strongest effects on both basal and TCDD-inducible activity. EMSA and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays further confirmed that both AhR and Nrf2 bind to the proximal promoter of MRP4. Our findings indicate that AhR and Nrf2 play important roles in regulating MRP4 expression and suggest that agents that activate their activity may be of therapeutic benefit for cholestasis.
Figures
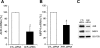

References
-
- Aleksunes LM, Slitt AL, Maher JM, Dieter MZ, Knight TR, Goedken M, Cherrington NJ, Chan JY, Klaassen CD, Manautou JE. Nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 expression in liver is critical for induction of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 during cholestasis. Cell Stress Chaperones 11: 356–363, 2006 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Assem M, Schuetz EG, Leggas M, Sun D, Yasuda K, Reid G, Zelcer N, Adachi M, Strom S, Evans RM, Moore DD, Borst P, Schuetz JD. Interactions between hepatic Mrp4 and Sult2a as revealed by the constitutive androstane receptor and Mrp4 knockout mice. J Biol Chem 279: 22250–22257, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Auyeung DJ, Kessler FK, Ritter JK. Mechanism of rat UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A6 induction by oltipraz: evidence for a contribution of the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway. Mol Pharmacol 63: 119–127, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Belinsky MG, Dawson PA, Shchaveleva I, Bain LJ, Wang R, Ling V, Chen ZS, Grinberg A, Westphal H, Klein-Szanto A, Lerro A, Kruh GD. Analysis of the in vivo functions of Mrp3. Mol Pharmacol 68: 160–168, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

