VIP/PACAP receptor mediation of cutaneous active vasodilation during heat stress in humans
- PMID: 20395540
- PMCID: PMC2904198
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01187.2009
VIP/PACAP receptor mediation of cutaneous active vasodilation during heat stress in humans
Abstract
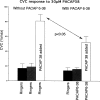
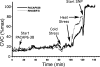
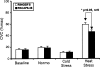
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is implicated in cutaneous active vasodilation in humans. VIP and the closely related pituitary adenylate cyclase activating peptide (PACAP) act through several receptor types: VIP through VPAC1 and VPAC2 receptors and PACAP through VPAC1, VPAC2, and PAC1 receptors. We examined participation of VPAC2 and/or PAC1 receptors in cutaneous vasodilation during heat stress by testing the effects of their specific blockade with PACAP6-38. PACAP6-38 dissolved in Ringer's was administered by intradermal microdialysis at one forearm site while a control site received Ringer's solution. Skin blood flow was monitored by laser-Doppler flowmetry (LDF). Blood pressure was monitored noninvasively and cutaneous vascular conductance (CVC) calculated. A 5- to 10-min baseline period was followed by approximately 70 min of PACAP6-38 (100 microM) perfusion at one site in normothermia and a 3-min period of body cooling. Whole body heating was then performed to engage cutaneous active vasodilation and was maintained until CVC had plateaued at an elevated level at all sites for 5-10 min. Finally, 58 mM sodium nitroprusside was perfused through both microdialysis sites to effect maximal vasodilation. No CVC differences were found between control and PACAP6-38-treated sites during normothermia (19 +/- 3%max untreated vs. 20 +/- 3%max, PACAP6-38 treated; P > 0.05 between sites) or cold stress (11 +/- 2%max untreated vs. 10 +/- 2%max, PACAP6-38 treated, P > 0.05 between sites). PACAP6-38 attenuated the increase in CVC during whole body heating when compared with untreated sites (59 +/- 3%max untreated vs. 46 +/- 3%max, PACAP6-38 treated, P < 0.05). We conclude that VPAC2 and/or PAC1 receptor activation is involved in cutaneous active vasodilation in humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide and receptors for VIP and PACAP in cutaneous active vasodilation during heat stress in humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Nov;113(10):1512-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00859.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 6. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22961270
-
Stimulatory effect of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide 6-38, M65 and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide 6-28 on trigeminal sensory neurons.Neuroscience. 2015 Nov 12;308:144-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.043. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26321242
-
Roles of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in cutaneous vasodilation induced by local warming of the skin and whole body heat stress in humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Nov;107(5):1438-44. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00690.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009. PMID: 19745188 Free PMC article.
-
Role of VIP and PACAP in islet function.Peptides. 2007 Sep;28(9):1805-13. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.04.024. Epub 2007 May 6. Peptides. 2007. PMID: 17559974 Review.
-
PACAP and its receptors in cranial arteries and mast cells.J Headache Pain. 2018 Feb 20;19(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0822-2. J Headache Pain. 2018. PMID: 29460121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thermal dysregulation in patients with multiple sclerosis during SARS-CoV-2 infection. The potential therapeutic role of exercise.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022 Mar;59:103557. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.103557. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 35092946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A clinical randomized controlled trial: moxibustion at Laogong interval with Panax notoginseng promoted the maturation of arteriovenous fistulae.Chin Med. 2022 Apr 20;17(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00604-9. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35443733 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediates the nitric oxide component of reflex cutaneous vasodilatation during dynamic exercise in humans.J Physiol. 2014 Dec 1;592(23):5317-26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.272898. Epub 2014 Sep 25. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25260636 Free PMC article.
-
Intradermal administration of ATP augments methacholine-induced cutaneous vasodilation but not sweating in young males and females.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Oct 15;309(8):R912-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00261.2015. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26290105 Free PMC article.
-
PACAP Attenuates Optic Nerve Crush-Induced Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis Via Activation of the CREB-Bcl-2 Pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jul;68(3):475-484. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01309-9. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30993644
References
-
- Anderson C, Andersson T, Wardell K. Changes in skin circulation after insertion of a microdialysis probe visualized by laser-Doppler perfusion imaging. J Invest Dermatol 102: 808– 811, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Cui J, Sathishkumar M, Wilson TE, Shibasaki M, Davis SL, Crandall CG. Spectral characteristics of skin sympathetic nerve activity in heat-stressed humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290: H1601– H1609, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Delgado M, Pozo D, Ganea D. The significance of vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation. Pharmacol Rev 56: 249– 290, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

