Characterization of expression of glycan ligands for Siglec-F in normal mouse lungs
- PMID: 20395633
- PMCID: PMC3049235
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0007OC
Characterization of expression of glycan ligands for Siglec-F in normal mouse lungs
Abstract
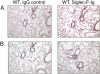
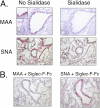
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec)-F, an inhibitory receptor on mouse eosinophils, preferentially recognizes the glycan ligand 6'-sulfated sialyl Lewis X, but little is known about the requirements for its lung expression. RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry were used to detect and localize the sulfotransferase keratin sulfate galactose 6-O sulfotransferase (KSGal6ST, also known as carbohydrate sulfotransferase 1; gene name, Chst1) that is putatively required for 6'-sulfated Sialyl Lewis X synthesis. RT-PCR detected the greatest constitutive expression of Chst1 in lung, liver, and spleen tissue. Immunohistochemistry localized the expression of KSGal6ST in lung tissue primarily to airway epithelium. Siglec-F-Ig fusion protein selectively bound in a similar pattern, and was unaffected in lung tissue treated with methanol or deficient in Type 2 α2,3 sialyltransferase (St3gal2), but was eliminated by proteinase K or sialidase, and was absent in tissue deficient in the Type 3 α2,3 sialyltransferase (St3gal3). Binding of the Siglec-F-Ig fusion protein was similar in pattern to, and completely blocked by, a plant lectin recognizing α2,3-linked sialic acid. Thus, α2,3-linked sialic acid-containing glycoprotein Siglec-F ligands and the enzymes required for their synthesis are constitutively expressed in murine lungs, especially by airway epithelium. St3gal3, but not St3gal2, is required for constitutive Siglec-F ligand synthesis. The survival of eosinophils entering the lung may be shortened by encountering these Siglec-F sialoside ligands.
Figures

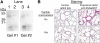


Similar articles
-
The role of lung epithelial ligands for Siglec-8 and Siglec-F in eosinophilic inflammation.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;13(1):106-11. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32835b594a. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23160308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mice deficient in the St3gal3 gene product α2,3 sialyltransferase (ST3Gal-III) exhibit enhanced allergic eosinophilic airway inflammation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Jan;133(1):240-7.e1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 Jul 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23830412 Free PMC article.
-
Airway glycomic and allergic inflammatory consequences resulting from keratan sulfate galactose 6-O-sulfotransferase (CHST1) deficiency.Glycobiology. 2018 Jun 1;28(6):406-417. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwy025. Glycobiology. 2018. PMID: 29659839 Free PMC article.
-
Galactose 6-O-sulfotransferases are not required for the generation of Siglec-F ligands in leukocytes or lung tissue.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 13;288(37):26533-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.485409. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23880769 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-8 on human eosinophils and mast cells, and Siglec-F on murine eosinophils, are functionally related inhibitory receptors.Clin Exp Allergy. 2009 Mar;39(3):317-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03173.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19178537 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers of eosinophil involvement in allergic and eosinophilic diseases: review of phenotypic and serum markers including a novel assay to quantify levels of soluble Siglec-8.J Immunol Methods. 2012 Sep 28;383(1-2):39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2012.05.017. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Immunol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22683541 Free PMC article.
-
Glycobiology of Eosinophilic Inflammation: Contributions of Siglecs, Glycans, and Other Glycan-Binding Proteins.Front Med (Lausanne). 2017 Aug 2;4:116. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2017.00116. eCollection 2017. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28824909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lung epithelial ligands for Siglec-8 and Siglec-F in eosinophilic inflammation.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;13(1):106-11. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32835b594a. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23160308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early murine T-lymphocyte activation is accompanied by a switch from N-Glycolyl- to N-acetyl-neuraminic acid and generation of ligands for siglec-E.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 7;286(40):34522-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.243410. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21835922 Free PMC article.
-
Sialic acids as cellular markers of immunomodulatory action of dexamethasone on glioma cells of different immunogenicity.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 May;455(1-2):147-157. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3478-6. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30443853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kikly KK, Bochner BS, Freeman S, Tan KB, Gallagher KT, D'Alessio K, Holmes SD, Abrahamson J, Hopson CB, Fischer EI, et al. Identification of SAF-2, a novel Siglec expressed on eosinophils, mast cells and basophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000;105:1093–1100. - PubMed
-
- Floyd H, Ni J, Cornish AL, Zeng Z, Liu D, Carter KC, Steel J, Crocker PR. Siglec-8: a novel eosinophil-specific member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem 2000;275:861–866. - PubMed
-
- Varki A, Angata T. Siglecs: the major sub-family of I-type lectins. Glycobiology 2006;16:1R–27R. - PubMed
-
- Crocker PR, Paulson JC, Varki A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2007;7:255–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

