Diet and age interactions with regards to cholesterol regulation and brain pathogenesis
- PMID: 20396385
- PMCID: PMC2852598
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/219683
Diet and age interactions with regards to cholesterol regulation and brain pathogenesis
Abstract
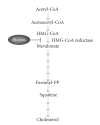
Cholesterol is an essential molecule for brain homeostasis; yet, hypercholesterolemia and its numerous complications are believed to play a role in promoting multiple aspects of brain pathogenesis. An ever increasing number of individuals in modern Western Society are regularly consuming diets high in fat which promote the development of hypercholesterolemia. Additionally, modern societies are becoming increasingly aged, causing a collision between increased hypercholesterolemia and increased aging, which will likely lead to the development of increased pathological conditions due to hypercholesterolemia, thereby promoting deleterious neurochemical and behavioral changes in the brain. Lastly, while beneficial in controlling cholesterol levels, the long-term use of statins itself may potentially promote adverse effects on brain homeostasis, although specifics on this remain largely unknown. This review will focus on linking the current understanding of diet-induced hypercholesterolemia (as well as statin use) to the development of oxidative stress, neurochemical alterations, and cognitive disturbances in the aging brain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intersection between metabolic dysfunction, high fat diet consumption, and brain aging.J Neurochem. 2010 Jul;114(2):344-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06803.x. Epub 2010 May 6. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20477933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in astrocyte functional markers and β-amyloid metabolism-related proteins in the early stages of hypercholesterolemia.Neuroscience. 2016 Mar 1;316:178-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.12.039. Epub 2015 Dec 24. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26724580
-
Keep recycling going: New approaches to reduce LDL-C.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;164:336-341. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30953636 Review.
-
MicroRNA-25-dependent up-regulation of NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) mediates hypercholesterolemia-induced oxidative/nitrative stress and subsequent dysfunction in the heart.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Sep;62:111-21. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 May 27. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23722270
-
High Cholesterol Diet Exacerbates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in LDLr-/- Mice: Impact on Cognitive Function.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;78(1):97-115. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200541. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32925052 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
'Saba' banana (Musa acuminata x balbisiana BBB Group) peel pectin supplementation improves biomarkers of obesity and associated blood lipid disorders in obese hypercholesterolemic mice.Curr Res Food Sci. 2022 Jan 25;5:251-260. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.01.016. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 35146442 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of the Global Diet Quality Score with Nutrition and Health Outcomes in Mexico with 24-h Recall and FFQ Data.J Nutr. 2021 Oct 23;151(12 Suppl 2):143S-151S. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab202. J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34689195 Free PMC article.
-
Damaging effects of a high-fat diet to the brain and cognition: a review of proposed mechanisms.Nutr Neurosci. 2014 Nov;17(6):241-51. doi: 10.1179/1476830513Y.0000000092. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Nutr Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24192577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health assessment and seroepidemiologic survey of potential pathogens in wild Antillean manatees (Trichechus manatus manatus).PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044517. Epub 2012 Sep 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984521 Free PMC article.
-
Increase of arginase activity in old apolipoprotein-E deficient mice under Western diet associated with changes in neurovascular unit.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jun 18;9:132. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-132. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22709928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu J-P, Tang Y, Zhou S, Toh BH, McLean C, Li H. Cholesterol involvement in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience. 2010;43(1):33–42. - PubMed
-
- Anzalone DA, Anzalone FL, Fos PJ. High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol: determining hygienic factors for intervention. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 1995;37(7):856–861. - PubMed
-
- Schaefer EJ. New recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of plasma lipid abnormalities. Nutrition Reviews. 1993;51(8):246–253. - PubMed
-
- Mourao PAS, Bracamonte CA. The binding of human aortic glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans to plasma low density lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1984;50(2):133–146. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

