Surgical, orthodontic and prosthodontic rehabilitation of a patient with follicular ameloblastoma: a case report
- PMID: 20396452
- PMCID: PMC2853834
Surgical, orthodontic and prosthodontic rehabilitation of a patient with follicular ameloblastoma: a case report
Abstract
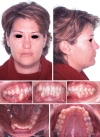
This case report describes the combined surgical, orthodontic and prosthodontic rehabilitation of an adult female patient with a previous history of follicular ameloblastoma, which was treated through partial mandibulectomy and an immediate replacement of missing bone with an autologous calvarial bone graft. Orthodontic treatment was undertaken in order to restore occlusal disturbances and obtain sufficient space for two dental implants and an optimum prosthodontic rehabilitation.
Keywords: Bone graft; Follicular ameloblastoma; Mandibulectomy; Orthodontic treatment.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Immediate Oral Rehabilitation Using Dental Implants After Marginal Mandibulectomy: A Case Report.J Oral Implantol. 2020 Feb 1;46(1):73-79. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-19-00143. J Oral Implantol. 2020. PMID: 31815591
-
Mandibular reconstruction with autologous human bone marrow stem cells and autogenous bone graft in a patient with plexiform ameloblastoma.J Craniofac Surg. 2013 Jul;24(4):e409-11. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318292c91d. J Craniofac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23851884
-
Rehabilitation with dental implants in microvascular iliac graft after solid ameloblastoma resection: a case report.Implant Dent. 2013 Dec;22(6):561-5. doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000007. Implant Dent. 2013. PMID: 24168903
-
Occlusal rehabilitation using implants for orthodontic anchorage.J Prosthodont. 1998 Dec;7(4):232-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-849x.1998.tb00211.x. J Prosthodont. 1998. PMID: 10196843
-
Alveolar Bone Grafting in Cleft Patients from Bone Defect to Dental Implants.Acta Stomatol Croat. 2014 Dec;48(4):250-7. doi: 10.15644/asc47/4/2. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2014. PMID: 27688373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of β-catenin and AXIN2 in ameloblastomas.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2013;17(3):250-6. doi: 10.5114/wo.2013.35278. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2013. PMID: 24596510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Junquera L, Ascani G, Vicente JC, Garcia-Consuegra L, Roig P. Ameloblastoma revisited. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2003;112:1034–1039. - PubMed
-
- Gorlin RJ, Chaudhry AP, Pindborg JJ. Odontogenic tumors: Classification, histopathology clinical behaviour in man and domesticated animals. Cancer. 1961;14:73–101. - PubMed
-
- Adekeye EO. Ameloblastoma of jaws: A survey of 109 Nigerian patients. J Oral Surg. 1980;38:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Adekeye EO, Lavery KM. Recurrent ameloblastoma of the maxillofacial region. Clinical features and treatment. J Maxillofac Surg. 1986;14:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Reichart PA, Philipsen HP, Sonner S. Ameloblastoma: biological profile of 3677 cases. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1995;31:86–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
