The Effect of Paroxetine on the Reduction of Migraine Frequency is Independent of Its Anxiolytic Effect
- PMID: 20396527
- PMCID: PMC2854974
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2006.2.4.246
The Effect of Paroxetine on the Reduction of Migraine Frequency is Independent of Its Anxiolytic Effect
Abstract
Background and purpose: Anxiety is the most important precipitating factor of migraine attacks, and more than half of migraineurs have coexisting anxiety disorders. Paroxetine, an antidepressant, is one of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) that has an anxiolytic effect, and is also known to be effective for migraine prophylaxis. The aim of this study was to determine the role of the anxiolytic effect of paroxetine on the prevention of migraine.
Methods: This study investigated migraineurs with a general anxiety disorder who visited the neurological clinic. The following efficacy variables were assessed at baseline and after taking paroxetine (20 for 12 weeks: headache frequency, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Headache Management Self-Efficacy Scale (HMSE), and Headache Disability Inventory (HDI). The correlation between the headache responsiveness to paroxetine and improvement in anxiety levels was analyzed.
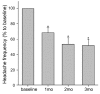
Results: Twenty-four patients (aged 54.96+/-12.09 years, mean+/-SD) were included in this study. Paroxetine reduced headache frequency by 49.1% within 12 weeks (p<0.05 vs baseline). HAM-A and HMSE scores also showed an improvement, whereas there was no significant change in HDI score. The baseline HAM-A scores did not differ between paroxetine responders and nonresponders. In addition, the improvement in HAM-A score was not correlated with the reduction in headache frequency.
Conclusions: Paroxetine decreased the headache frequency and reduced anxiety levels. However, the anxiolytic effect of paroxetine was not correlated with the migraine prevention effect. These observation indicate that the anxiolytic effect of paroxetine does not contribute strongly to its prophylactic effect on migraine frequency in migraineurs with anxiety disorder.
Keywords: Anxiety disorder; Headache frequency; Migraine; Paroxetine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of the 5-HT1A agonist, buspirone hydrochloride, in migraineurs with anxiety: a randomized, prospective, parallel group, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Headache. 2005 Sep;45(8):1004-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05181.x. Headache. 2005. PMID: 16109114 Clinical Trial.
-
Depression and anxiety: effect on the migraine-obesity relationship.Headache. 2007 Jun;47(6):866-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00810.x. Headache. 2007. PMID: 17578537
-
Potential benefits of slow titration of paroxetine treatment in an elderly population: eight-week results from a naturalistic setting.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013 Aug;33(4):565-9. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182905967. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23764690 Clinical Trial.
-
Paroxetine: an update of its use in psychiatric disorders in adults.Drugs. 2002;62(4):655-703. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262040-00010. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11893234 Review.
-
The Migraine-Anxiety Comorbidity Among Migraineurs: A Systematic Review.Front Neurol. 2021 Jan 18;11:613372. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.613372. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33536997 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antidepressants for Preventive Treatment of Migraine.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019 Mar 21;21(4):18. doi: 10.1007/s11940-019-0557-2. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30895388 Review.
-
Acute and Preventive Management of Migraine during Menstruation and Menopause.J Clin Med. 2021 May 24;10(11):2263. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112263. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34073696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Italian guidelines for primary headaches: 2012 revised version.J Headache Pain. 2012 May;13 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S31-70. doi: 10.1007/s10194-012-0437-6. J Headache Pain. 2012. PMID: 22581120 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal anti-CGRP antibodies in post-menopausal women: a real-life study.Acta Neurol Belg. 2023 Jun;123(3):1039-1047. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02190-5. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Acta Neurol Belg. 2023. PMID: 36867346
-
Paroxetine increases delta opioid responsiveness in sensory neurons.eNeuro. 2022 Jul 25;9(4):ENEURO.0063-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0063-22.2022. Online ahead of print. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35882549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breslau N, Rasmussen BK. The impact of migraine: Epidemiology, risk factors, and co-morbidities. Neurology. 2001;56:S4–S12. - PubMed
-
- Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Young YH, Lu SR, Shia BC. Prevalence of migraine in Taipei, Taiwan: a population-based survey. Cephalalgia. 2000;20:566–572. - PubMed
-
- Sakai F, Igarashi H. Prevalence of migraine in Japan: a nationwide survey. Cephalalgia. 1997;17:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Roh JK, Kim JS, Ahn YO. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of migraine and tension-type headache in Korea. Headache. 1998;38:356–365. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

