Downbeat, positional, and perverted head-shaking nystagmus associated with lamotrigine toxicity
- PMID: 20396535
- PMCID: PMC2854982
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2006.2.4.283
Downbeat, positional, and perverted head-shaking nystagmus associated with lamotrigine toxicity
Abstract
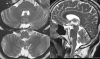
Lamotrigine is an effective antiepileptic drug with few adverse effects. Nystagmus is one of the commonly observable signs of lamotrigine overdose, which may result from central nervous system involvement. However, the physiologic basis of lamotrigine-induced nystagmus is not fully understood. Here we report a patient who presented with lamotrigine-associated nystagmus that was probably related to cerebellar dysfunction.
Keywords: Downbeat nystagmus; Lamotrigine toxicity; Perverted head-shaking nystagmus.
Figures
References
-
- Alkawi A, Kattah JC, Wyman K. Downbeat nystagmus as a result of lamotrigine toxicity. Epilepsy Res. 2005;63:85–88. - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell J, Bateman DN. Lamotrigine overdose in an adult. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2000;38:659–660. - PubMed
-
- Leigh RJ, Zee DS. The Neurology of Eye Movements. 4th edn. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006. pp. 274–280.
-
- Zee DS, Yamazaki A, Butler PH, Gucer G. Effects of ablation of flocculus and paraflocculus on eye movements in primate. J Neurophysiol. 1981;46:878–899. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez C, Alzate R, Lindsay JR. Experimental observations on postural nystagmus. Lesions of the nodulus. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1960;69:94–114. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources