Omega-3 fatty acids: potential role in the management of early Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20396634
- PMCID: PMC2854051
- DOI: 10.2147/cia.s5231
Omega-3 fatty acids: potential role in the management of early Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain growth and development. They play an important role throughout life, as critical modulators of neuronal function and regulation of oxidative stress mechanisms, in brain health and disease. Docosahexanoic acid (DHA), the major omega-3 fatty acid found in neurons, has taken on a central role as a target for therapeutic intervention in Alzheimer's disease (AD). A plethora of in vitro, animal model, and human data, gathered over the past decade, highlight the important role DHA may play in the development of a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders, including AD. Cross sectional and prospective cohort data have demonstrated that reduced dietary intake or low brain levels of DHA are associated with accelerated cognitive decline or the development of incipient dementia, including AD. Several clinical trials investigating the effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in AD have been completed and all failed to demonstrate its efficacy in the treatment of AD. However, these trials produced intriguing data suggesting that the beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation may depend on the stage of disease, other dietary mediators, and apolipoprotein E status.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; clinical studies; omega-3 fatty acids; oxidative stress; treatment.
Figures
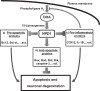

References
-
- Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2009;5(3):234–270. - PubMed
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology. 1984;34(7):939–944. - PubMed
-
- Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18(4 Suppl):S1–S2. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1991;82(4):239–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

