Ribosomal P autoantibodies are present before SLE onset and are directed against non-C-terminal peptides
- PMID: 20396862
- PMCID: PMC2877769
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-010-0618-1
Ribosomal P autoantibodies are present before SLE onset and are directed against non-C-terminal peptides
Abstract
Autoantibodies to ribosomal P (ribo P) are found in 15-30% of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and are highly specific for SLE. The goal of this study is to assess the temporal association of anti-ribosomal P (anti-P) responses with SLE disease onset, as well as to characterize select humoral ribo P epitopes targeted in early, pre-diagnostic SLE samples. Patients with stored serial serum samples available prior to SLE diagnosis were identified from a military cohort. Each sample was tested for antibodies against ribo P utilizing standard C terminus ribo P enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and a solid phase, bead-based assay with affinity-purified ribo P proteins. In this study, antibodies to ribo P were more common in African American SLE patients (p = 0.026), and anti-P-positive patients comprised a group with more measured autoantibody specificities than did other SLE patients (3.5 vs 2.2, p < 0.05). Antibodies against ribo P were present on average 1.7 years before SLE diagnosis and were detected an average of 1.08 years earlier in pre-diagnostic SLE samples using affinity-purified whole protein rather than C-terminal peptide alone (p = 0.0019). Furthermore, 61% of anti-P-positive patients initially had antibodies to aa 99-113, a known ribosomal P0 antigenic target, at a time point when no antibodies to the clinically used C terminus were detected. Our findings provide evidence that antibodies against ribosomal P frequently develop before clinical SLE diagnosis and are more broadly reactive than previously thought by targeting regions outside of the C terminus.
Figures
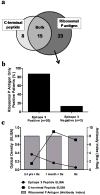
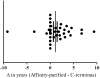
References
-
- Ghirardello A, Doria A, Zampieri S, Gerli R, Rapizzi E, Gambari PF. Anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies detected by immunoblotting in patients with connective tissue diseases: their specificity for SLE and association with IgG anticardiolipin antibodies. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2000;59:975–981. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hanly JG, Urowitz MB, Siannis F, Farewell V, Gordon C, Bae SC, Isenberg D, Dooley MA, Clarke A, Bernatsky S, Gladman D, Fortin PR, Manzi S, Steinsson K, Bruce IN, Ginzler E, Aranow C, Wallace DJ, Ramsey-Goldman R, van Vollenhoven R, Sturfelt G, Nived O, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Alarcon GS, Petri M, Khamashta M, Zoma A, Font J, Kalunian K, Douglas J, Qi Q, Thompson K, Merrill JT. Autoantibodies and neuropsychiatric events at the time of systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis: results from an international inception cohort study. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2008;58:843–853. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonfa E, Golombek SJ, Kaufman LD, Skelly S, Weissbach H, Brot N, Elkon KB. Association between lupus psychosis and anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:265–271. - PubMed
-
- Briani C, Lucchetta M, Ghirardello A, Toffanin E, Zampieri S, Ruggero S, Scarlato M, Quattrini A, Bassi N, Ermani M, Battistin L, Doria A. Neurolupus is associated with anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies: an inception cohort study. Journal of autoimmunity. 2009;32:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Nasser AM, Ghaleb RM, Mahmoud JA, Khairy W, Mahmoud RM. Association of anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies with neuropsychiatric and other manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical rheumatology. 2008;27:1377–1385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AR045231/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR45231/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR045084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR14467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI24717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR58554/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR014467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AR53483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR048940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR045451/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047575/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR45451/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI31584/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103510/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR42460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR15577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AR45084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI82714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058554/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR20143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI031584/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 RR031152/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI47575/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR48045/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR048045/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007633/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR48940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

