Obovatol attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation by modulating redox regulation
- PMID: 20397299
- PMCID: PMC2925488
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00659.x
Obovatol attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation by modulating redox regulation
Abstract
Background and purpose: Obovatol isolated from the medicinal herb Magnolia obovata exhibits a variety of biological activities. Here, the effect of obovatol and its mechanism of action on microglial activation, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration were investigated.
Experimental approach: In microglial BV-2 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), we measured nitric oxide (NO) and cytokine production, and activation of intracellular signalling pathways by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blots. Cell death was assayed in co-cultures of activated microglia (with bacterial LPS) and neurons and in LPS- induced neuroinflammation in mice in vivo.
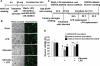
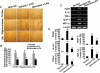
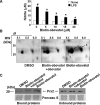
Key results: Obovatol inhibited microglial NO production with an IC50 value of 10 mM. Obovatol also inhibited microglial expression of proinflammatory cytokines and inducible nitric-oxide synthase, which was accompanied by the inhibition of multiple signalling pathways such as nuclear factor kappa B, signal transducers and activators of transcription 1, and mitogen-activated protein kinases. In addition, obovatol protected cultured neurons from microglial toxicity and inhibited neuroinflammation in mice in vivo. One molecular target of obovatol in microglia was peroxiredoxin 2 (Prx2), identified by affinity chromatography and mass spectrometry. Obovatol enhanced the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging activity of Prx2 in vitro, thereby suppressing proinflammatory signalling pathways of microglia where ROS plays an important role.
Conclusions and implications: Obovatol is not only a useful chemical tool that can be used to investigate microglial signalling, but also a promising drug candidate against neuroinflammatory diseases. Furthermore, our results indicate that Prx2 is a novel drug target that can be exploited for the therapeutic modulation of neuroinflammatory signalling.
Figures









References
-
- Araki W, Yuasa K, Takeda S, Shirotani K, Takahashi K, Tabira T. Overexpression of presenilin-2 enhances apoptotic death of cultured cortical neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;920:241–244. - PubMed
-
- Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, Kim JY, Abraham E. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 2004;172:2522–2529. - PubMed
-
- Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC, Hogan EL. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J Neurosci. 1998;18:1633–1641. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blasi E, Barluzzi R, Bocchini V, Mazzolla R, Bistoni F. Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J Neuroimmunol. 1990;27:229–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

