NMR characterization of the interaction of the Salmonella type III secretion system protein SipD and bile salts
- PMID: 20397637
- PMCID: PMC3721326
- DOI: 10.1021/bi100335u
NMR characterization of the interaction of the Salmonella type III secretion system protein SipD and bile salts
Abstract
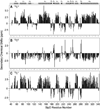
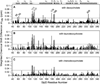
Salmonella and Shigella bacteria require the type III secretion system (T3SS) to inject virulence proteins into their hosts and initiate infections. The tip proteins SipD and IpaD are critical components of the Salmonella and Shigella T3SS, respectively. Recently, SipD and IpaD have been shown to interact with bile salts, which are enriched in the intestines, and are hypothesized to act as environmental sensors for these enteric pathogens. Bile salts activate the Shigella T3SS but repress the Salmonella T3SS, and the mechanism of this differing response to bile salts is poorly understood. Further, how SipD binds to bile salts is currently unknown. Computer modeling predicted that IpaD binds the bile salt deoxycholate in a cleft formed by the N-terminal domain and the long central coiled coil of IpaD. Here, we used NMR methods to determine which SipD residues are affected by the interaction with the bile salts deoxycholate, chenodeoxycholate, and taurodeoxcholate. The bile salts perturbed nearly the same set of SipD residues; however, the largest chemical shift perturbations occurred away from what was predicted for the bile salt binding site in IpaD. Our NMR results indicate that that bile salt interaction of SipD will be different from what was predicted for IpaD, suggesting a possible mechanism for the differing response of Salmonella and Shigella to bile salts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NMR identification of the binding surfaces involved in the Salmonella and Shigella Type III secretion tip-translocon protein-protein interactions.Proteins. 2016 Aug;84(8):1097-107. doi: 10.1002/prot.25055. Epub 2016 May 5. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 27093649 Free PMC article.
-
The crystal structures of the Salmonella type III secretion system tip protein SipD in complex with deoxycholate and chenodeoxycholate.Protein Sci. 2011 Jan;20(1):75-86. doi: 10.1002/pro.537. Protein Sci. 2011. PMID: 21031487 Free PMC article.
-
NMR model of PrgI-SipD interaction and its implications in the needle-tip assembly of the Salmonella type III secretion system.J Mol Biol. 2014 Aug 12;426(16):2958-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 18. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24951833 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical basis for activation of virulence genes by bile salts in Vibrio parahaemolyticus.Gut Microbes. 2017 Jul 4;8(4):366-373. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1287655. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Gut Microbes. 2017. PMID: 28129014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures of Type III Secretion System Needle Filaments.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2020;427:109-131. doi: 10.1007/82_2019_192. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31974760 Review.
Cited by
-
Reassessment of MxiH subunit orientation and fold within native Shigella T3SS needles using surface labelling and solid-state NMR.J Struct Biol. 2015 Dec;192(3):441-448. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Oct 6. J Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 26439285 Free PMC article.
-
NMR identification of the binding surfaces involved in the Salmonella and Shigella Type III secretion tip-translocon protein-protein interactions.Proteins. 2016 Aug;84(8):1097-107. doi: 10.1002/prot.25055. Epub 2016 May 5. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 27093649 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi and Typhimurium Reveals Typhoidal Serovar-Specific Responses to Bile.Infect Immun. 2018 Feb 20;86(3):e00490-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00490-17. Print 2018 Mar. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29229736 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial type III secretion systems: a complex device for the delivery of bacterial effector proteins into eukaryotic host cells.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018 Oct 1;365(19):fny201. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny201. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30107569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three-dimensional electron microscopy reconstruction and cysteine-mediated crosslinking provide a model of the type III secretion system needle tip complex.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jan;95(1):31-50. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12843. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25353930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cornelis GR. The type III secretion injectisome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006;4:811–825. - PubMed
-
- Mueller CA, Broz P, Muller SA, Ringler P, Erne-Brand F, Sorg I, Kuhn M, Engel A, Cornelis GR. The V-antigen of Yersinia forms a distinct structure at the tip of injectisome needles. Science. 2005;310:674–676. - PubMed
-
- Stevens MP, Haque A, Atkins T, Hill J, Wood MW, Easton A, Nelson M, Underwood-Fowler C, Titball RW, Bancroft GJ, Galyov EE. Attenuated virulence and protective efficacy of a Burkholderia pseudomallei bsa type III secretion mutant in murine models of melioidosis. Microbiology. 2004;150:2669–2676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

