B cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients show important alterations in the expression of CD86 and FcgammaRIIb, which are modulated by anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy
- PMID: 20398308
- PMCID: PMC2888223
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2985
B cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients show important alterations in the expression of CD86 and FcgammaRIIb, which are modulated by anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy
Abstract
Introduction: Several molecules help preserve peripheral B cell tolerance, but when altered, they may predispose to autoimmunity. This work studied the expression of the costimulatory molecule CD86 and the inhibitory receptor for IgG immune complexes FcgammaRIIb (CD32b), on B cells from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and the influence of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) therapy.
Methods: Peripheral B cells from 18 RA patients and 13 healthy donors were characterized using flow cytometry. Eleven patients who underwent a six-month adalimumab therapy were further assessed for phenotypic changes on their B cells.
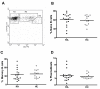
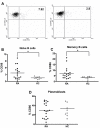
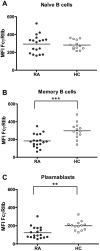
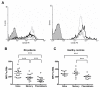
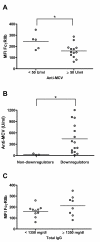
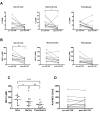
Results: RA patients exhibited a high percentage of naïve and memory B cells expressing CD86. In contrast, expression of FcgammaRIIb was significantly reduced on RA memory B cells and plasmablasts as compared to healthy donors, probably due to downregulation of this receptor when differentiating from naïve to memory cells. These alterations on FcgammaRIIb were associated with high levels of anti-citrullinated vimentin autoantibodies. In addition, treatment with adalimumab normalized the expression of CD86 on memory B cells and reduced the expression of FcgammaRIIb, mainly on naïve B cells.
Conclusions: Our findings show that peripheral B cells from RA patients have an altered expression of key molecules, such as CD86 and FcgammaRIIb. Because this latter receptor is required for feedback inhibition, a deficient expression might contribute to humoral autoimmune responses. Furthermore, these molecules are likely to be influenced by inflammatory factors, since they were modulated by TNF inhibition.
Figures
Comment in
-
Could the expression of CD86 and FcγRIIB on B cells be functionally related and involved in driving rheumatoid arthritis?Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):133. doi: 10.1186/ar3092. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20735866 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Suppression of rheumatoid arthritis B cells by XmAb5871, an anti-CD19 antibody that coengages B cell antigen receptor complex and Fcγ receptor IIb inhibitory receptor.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 May;66(5):1153-64. doi: 10.1002/art.38334. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24782179
-
Changes in macrophage function after rituximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2007 Jun;66(6):818-20. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.062505. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. PMID: 17148544 Free PMC article.
-
Preferential decrease in IgG4 anti-citrullinated protein antibodies during treatment with tumour necrosis factor blocking agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Apr;68(4):558-63. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.088401. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. PMID: 18445623
-
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapy for rheumatoid arthritis.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008 Dec;106(6):778-87. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.07.025. Epub 2008 Oct 19. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008. PMID: 18930662 Review.
-
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in the 21st century: targeting B-lymphocytes.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2006 Jan;156(1-2):61-7. doi: 10.1007/s10354-005-0241-x. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2006. PMID: 16465615 Review.
Cited by
-
High frequencies of activated B cells and T follicular helper cells are correlated with disease activity in patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Nov;174(2):212-20. doi: 10.1111/cei.12162. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23786438 Free PMC article.
-
Could the expression of CD86 and FcγRIIB on B cells be functionally related and involved in driving rheumatoid arthritis?Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):133. doi: 10.1186/ar3092. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20735866 Free PMC article.
-
Engagement of CD22 on B cells with the monoclonal antibody epratuzumab stimulates the phosphorylation of upstream inhibitory signals of the B cell receptor.J Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Jun;10(2):143-51. doi: 10.1007/s12079-016-0322-1. Epub 2016 Apr 28. J Cell Commun Signal. 2016. PMID: 27125377 Free PMC article.
-
High-dose methylprednisolone pulse therapy upregulated FcγRIIb expression on B cells in primary Sjögren's syndrome patients with thrombocytopenia.Clin Rheumatol. 2013 Dec;32(12):1783-90. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2344-x. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23917390
-
Follicular dendritic cells in health and disease.Front Immunol. 2012 Sep 21;3:292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00292. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23049531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korganow AS, Ji H, Mangialaio S, Duchatelle V, Pelanda R, Martin T, Degott C, Kikutani H, Rajewsky K, Pasquali JL, Benoist C, Mathis D. From systemic T cell self-reactivity to organ-specific autoimmune disease via immunoglobulins. Immunity. 1999;10:451–461. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80045-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takemura S, Klimiuk PA, Braun A, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. T cell activation in rheumatoid synovium is B cell dependent. J Immunol. 2001;167:4710–4718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

