Systemic vasculopathy with altered vasoreactivity in a transgenic mouse model of scleroderma
- PMID: 20398328
- PMCID: PMC2888224
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2986
Systemic vasculopathy with altered vasoreactivity in a transgenic mouse model of scleroderma
Abstract
Introduction: Vasculopathy, including altered vasoreactivity and abnormal large vessel biomechanics, is a hallmark of systemic sclerosis (SSc). However, the pathogenic link with other aspects of the disease is less clear. To assess the potential role of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) overactivity in driving these cardiovascular abnormalities, we studied a novel transgenic mouse model characterized by ligand-dependent activation of TGF-beta signaling in fibroblasts.
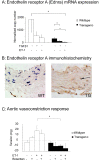
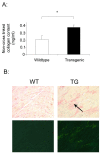
Methods: The transgenic mouse strain Tbeta RIIDeltak-fib is characterized by balanced ligand-dependent upregulation of TGF-beta signaling. Aortic and cardiac tissues were examined with histologic, biochemical, and isolated organ bath studies. Vascular and perivascular architecture was examined by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and special stains including immunostaining for TGF-beta1 and phospho-Smad2/3 (pSmad2/3). Confirmatory aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation, phenotype, and functional assays, including signaling responses to exogenous TGF-beta and endothelin-1, were performed. Aortic ring contractile responses to direct and receptor-mediated stimulation were assessed.
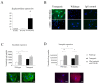
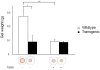
Results: Aortic ring contractility and relaxation were diminished compared with wild-type controls, and this was associated with aortic adventitial fibrosis confirmed histologically and with Sircol assay. TGF-beta1 and pSmad 2/3 expression was increased in the adventitia and smooth muscle layer of the aorta. Aortic smooth muscle cells from transgenic animals showed significant upregulation of TGF-beta- responsive genes important for cytoskeletal function, such as transgelin and smoothelin, which were then resistant to further stimulation with exogenous TGF-beta1. These cells promoted significantly more contraction of free floating type I collagen lattices when compared with the wild-type, but were again resistant to exogenous TGF-beta1 stimulation. Aortic ring responses to receptor-mediated contraction were reduced in the transgenic animals. Specifically, bosentan reduced endothelin-mediated contraction in wild-type animals, but had no effect in transgenic animals, and endothelin axis gene expression was altered in transgenic animals. Transgenic mice developed cardiac fibrosis.
Conclusions: The histologic, biochemical, and functional phenotype of this transgenic mouse model of scleroderma offers insight into the altered biomechanical properties previously reported for large elastic arteries in human SSc and suggests a role for perturbed TGF-beta and endothelin activity in this process.
Figures
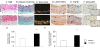
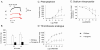
Comment in
-
Vascular alterations upon activation of TGFbeta signaling in fibroblasts--implications for systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(3):125. doi: 10.1186/ar3026. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20602813 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Gut fibrosis with altered colonic contractility in a mouse model of scleroderma.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012 Nov;51(11):1989-98. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes191. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 22908328
-
TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor-β) Signaling Protects the Thoracic and Abdominal Aorta From Angiotensin II-Induced Pathology by Distinct Mechanisms.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Nov;37(11):2102-2113. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309401. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28729364 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal induction of transforming growth factor beta signaling in fibroblasts of mice recapitulates clinical, histologic, and biochemical features of scleroderma.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Jan;56(1):334-44. doi: 10.1002/art.22328. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17195237
-
Animal models of scleroderma: lessons from transgenic and knockout mice.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009 Nov;21(6):630-5. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32833130c1. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19730378 Review.
-
Pathogenesis of scleroderma. Collagen.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996 Nov;22(4):647-74. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70294-5. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996. PMID: 8923589 Review.
Cited by
-
The pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor reduces development of lung fibrosis and attenuates cardiorespiratory manifestations in a transgenic mouse model of systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Sep 6;23(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02592-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34488870 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular alterations upon activation of TGFbeta signaling in fibroblasts--implications for systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(3):125. doi: 10.1186/ar3026. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20602813 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of transforming growth factor-β signaling in myeloid cells ameliorates aortic aneurysmal formation in Marfan syndrome.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 11;15(11):e0239908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239908. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33175881 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17A promotes functional activation of systemic sclerosis patient-derived dermal vascular smooth muscle cells by extracellular-regulated protein kinases signalling pathway.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Dec 31;16(6):4223. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0512-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25551434 Free PMC article.
-
Pinhole Descending Aortic Rupture with Systemic Sclerosis and Dermatomyositis: A Case Report.Ann Vasc Dis. 2024 Dec 25;17(4):437-439. doi: 10.3400/avd.cr.24-00108. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Ann Vasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 39726551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sfikakis PP, Papamichael C, Stamatelopoulos KS, Tousoulis D, Fragiadaki KG, Katsichti P, Stefanadis C, Mavrikakis M. Improvement of vascular endothelial function using the oral endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1985–1993. doi: 10.1002/art.22634. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

