Signal pathways JNK and NF-kappaB, identified by global gene expression profiling, are involved in regulation of TNFalpha-induced mPGES-1 and COX-2 expression in gingival fibroblasts
- PMID: 20398340
- PMCID: PMC2873473
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-241
Signal pathways JNK and NF-kappaB, identified by global gene expression profiling, are involved in regulation of TNFalpha-induced mPGES-1 and COX-2 expression in gingival fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is involved in several chronic inflammatory diseases including periodontitis, which causes loss of the gingival tissue and alveolar bone supporting the teeth. We have previously shown that tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) induces PGE2 synthesis in gingival fibroblasts. In this study we aimed to investigate the global gene expression profile of TNFalpha-stimulated primary human gingival fibroblasts, focusing on signal pathways related to the PGE2-synthesizing enzymes prostaglandin E synthases (PGES), as well as the upstream enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and PGE2 production.
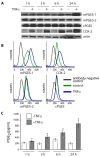
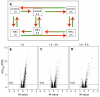
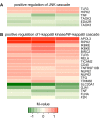
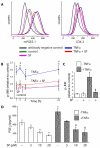
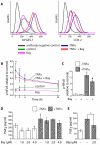
Results: Microarray and western blot analyses showed that the mRNA and protein expression of the inflammatory induced microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) was up-regulated by the cytokine TNFalpha, accompanied by enhanced expression of COX-2 and increased production of PGE2. In contrast, the expression of the isoenzymes microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-2 (mPGES-2) and cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase (cPGES) was unaffected by TNFalpha treatment. Using oligonucleotide microarray analysis in a time-course factorial design including time points 1, 3 and 6 h, differentially expressed genes in response to TNFalpha treatment were identified. Enrichment analysis of microarray data indicated two positively regulated signal transduction pathways: c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and Nuclear Factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). To evaluate their involvement in the regulation of mPGES-1 and COX-2 expression, we used specific inhibitors as well as phosphorylation analysis. Phosphorylation analysis of JNK (T183/Y185) and NF-kappaB p65 (S536) showed increased phosphorylation in response to TNFalpha treatment, which was decreased by specific inhibitors of JNK (SP600125) and NF-kappaB (Bay 11-7082, Ro 106-9920). Inhibitors of JNK and NF-kappaB also decreased the TNFalpha-stimulated up-regulation of mPGES-1 and COX-2 as well as PGE2 production.
Conclusion: In the global gene expression profile, the enrichment analysis of microarray data identified the two signal transduction pathways JNK and NF-kappaB as positively regulated by the cytokine TNFalpha. Inhibition of these TNFalpha-activated signal pathways reduced the expression of mPGES-1 and COX-2 as well as their end product PGE2 in gingival fibroblasts. The involvement of the signal pathways JNK and NF-kappaB in the regulation of PGE2 induced by TNFalpha may suggest these two pathways as possible attractive targets in the chronic inflammatory disease periodontitis.
Figures



References
-
- Bascones A, Noronha S, Gomez M, Mota P, Gonzalez Moles MA, Dorrego MV. Tissue destruction in periodontitis: bacteria or cytokines fault? Quintessence Int. 2005;36:299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

