Role of carnitine in disease
- PMID: 20398344
- PMCID: PMC2861661
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-7-30
Role of carnitine in disease
Abstract
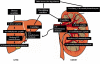
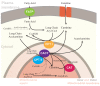
Carnitine is a conditionally essential nutrient that plays a vital role in energy production and fatty acid metabolism. Vegetarians possess a greater bioavailability than meat eaters. Distinct deficiencies arise either from genetic mutation of carnitine transporters or in association with other disorders such as liver or kidney disease. Carnitine deficiency occurs in aberrations of carnitine regulation in disorders such as diabetes, sepsis, cardiomyopathy, malnutrition, cirrhosis, endocrine disorders and with aging. Nutritional supplementation of L-carnitine, the biologically active form of carnitine, is ameliorative for uremic patients, and can improve nerve conduction, neuropathic pain and immune function in diabetes patients while it is life-saving for patients suffering primary carnitine deficiency. Clinical application of carnitine holds much promise in a range of neural disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, hepatic encephalopathy and other painful neuropathies. Topical application in dry eye offers osmoprotection and modulates immune and inflammatory responses. Carnitine has been recognized as a nutritional supplement in cardiovascular disease and there is increasing evidence that carnitine supplementation may be beneficial in treating obesity, improving glucose intolerance and total energy expenditure.
Figures
References
-
- De Vivo DC, Tein I. Primary and secondary disorders of carnitine metabolism. Int Pediatr. 1990;5:8.
-
- Rebouche CJ, Chenard CA. Metabolic fate of dietary carnitine in human adults: identification and quantification of urinary and fecal metabolites. J Nutr. 1991;121:539–546. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

