Multiphoton in vivo imaging of amyloid in animal models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20398680
- PMCID: PMC3117428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.04.007
Multiphoton in vivo imaging of amyloid in animal models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
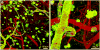
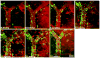
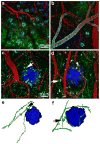
Amyloid-beta (Abeta) deposition is a defining feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The toxicity of Abeta aggregation is thought to contribute to clinical deficits including progressive memory loss and cognitive dysfunction. Therefore, Abeta peptide has become the focus of many therapeutic approaches for the treatment of AD due to its central role in the development of neuropathology of AD. In the past decade, taking the advantage of multiphoton microscopy and molecular probes for amyloid peptide labeling, the dynamic progression of Abeta aggregation in amyloid plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy has been monitored in real time in transgenic mouse models of AD. Moreover, amyloid plaque-associated alterations in the brain including dendritic and synaptic abnormalities, changes of neuronal and astrocytic calcium homeostasis, microglial activation and recruitment in the plaque location have been extensively studied. These studies provide remarkable insight to understand the pathogenesis and pathogenicity of amyloid plaques in the context of AD. The ability to longitudinally image plaques and related structures facilitates the evaluation of therapeutic approaches targeting toward the clearance of plaques.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Abramov AY, Canevari L, Duchen MR. Calcium signals induced by amyloid beta peptide and their consequences in neurons and astrocytes in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004b;1742:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Bacskai BJ, Hyman BT. Alzheimer’s disease: what multiphoton microscopy teaches us. Neuroscientist. 2002;8:386–390. - PubMed
-
- Bacskai BJ, Kajdasz ST, Christie RH, Carter C, Games D, Seubert P, Schenk D, Hyman BT. Imaging of amyloid-beta deposits in brains of living mice permits direct observation of clearance of plaques with immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2001;7:369–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

