3.3 A cryo-EM structure of a nonenveloped virus reveals a priming mechanism for cell entry
- PMID: 20398923
- PMCID: PMC3422562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.041
3.3 A cryo-EM structure of a nonenveloped virus reveals a priming mechanism for cell entry
Abstract
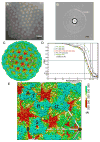
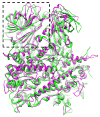
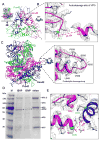
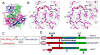
To achieve cell entry, many nonenveloped viruses must transform from a dormant to a primed state. In contrast to the membrane fusion mechanism of enveloped viruses (e.g., influenza virus), this membrane penetration mechanism is poorly understood. Here, using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy, we report a 3.3 A structure of the primed, infectious subvirion particle of aquareovirus. The density map reveals side-chain densities of all types of amino acids (except glycine), enabling construction of a full-atom model of the viral particle. Our structure and biochemical results show that priming involves autocleavage of the membrane penetration protein and suggest that Lys84 and Glu76 may facilitate this autocleavage in a nucleophilic attack. We observe a myristoyl group, covalently linked to the N terminus of the penetration protein and embedded in a hydrophobic pocket. These results suggest a well-orchestrated process of nonenveloped virus entry involving autocleavage of the penetration protein prior to exposure of its membrane-insertion finger.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Banerjee M, Johnson JE. Activation, exposure and penetration of virally encoded, membrane-active polypeptides during non-enveloped virus entry. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2008;9:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett GJ, Porter CT, Borkakoti N, Thornton JM. Analysis of catalytic residues in enzyme active sites. J Mol Biol. 2002;324:105–121. - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, et al. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1998;54:905–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

