Detection of increased scyllo-inositol in brain with magnetic resonance spectroscopy after dietary supplementation in Alzheimer's disease mouse models
- PMID: 20399219
- PMCID: PMC2926267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.03.011
Detection of increased scyllo-inositol in brain with magnetic resonance spectroscopy after dietary supplementation in Alzheimer's disease mouse models
Abstract
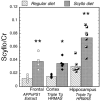
There is evidence that inositol isomers may help protect against formation of toxic fibrils of Abeta fragments in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Scyllo-inositol is one of the more promising inositol isomers for the potential treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and can be detected using MRS in human subjects. In this manuscript we demonstrate using MRS, in two different mouse models of AD (APP x PS1 and APP x PS1 x tau), that we could detect increased scyllo-inositol in the hippocampus and frontal cortex in mice fed water supplemented with 16.5 mg/L of scyllo-inositol equivalent to about 3.3 mg/kg/day. We used both brain extracts using solution MRS as well as intact brain tissue using high resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) to ensure that any membrane-associated scyllo-inositol would be detected. By brain extracts we detected a 3.0 fold increase in scyllo-inositol in the scyllo-fed AD mice compared to normal diet (p < 0.001). Using HRMAS we detected a 2.2-2.4-fold increase in scyllo-inositol (p < 0.001). Scyllo-inositol treatment was associated with an increase in glutamine in hippocampus. The concentrations of scyllo-inositol were higher in the hippocampus than in the frontal cortex. Mice have a smaller concentration of scyllo-inositol than humans (ca. 100 microM vs. 500 microM in humans). Given the ease with which scyllo-inositol can be measured in human MRS data with high signal to noise ratios, these data suggest that MRS will prove useful for evaluation of inositol treatment trials in AD subjects.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regional metabolic alteration of Alzheimer's disease in mouse brain expressing mutant human APP-PS1 by 1H HR-MAS.Behav Brain Res. 2010 Jul 29;211(1):125-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.03.026. Epub 2010 Mar 20. Behav Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20307581
-
Investigating the efficacy of a combination Aβ-targeted treatment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res. 2018 Jan 1;1678:138-145. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.10.015. Epub 2017 Oct 21. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29066368
-
Combination therapy in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease.Exp Neurol. 2013 Dec;250:228-238. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Exp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24120437 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted assessment of the APP/PS1 mouse model for Alzheimer's disease: Applying MRS, DTI, and ASL.Brain Res. 2018 Nov 1;1698:114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 30077647
-
scyllo-Inositol, preclinical, and clinical data for Alzheimer's disease.Adv Pharmacol. 2012;64:177-212. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394816-8.00006-4. Adv Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22840748 Review.
Cited by
-
High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton NMR Study of Alzheimer's Disease with Mouse Models.Metabolites. 2022 Mar 17;12(3):253. doi: 10.3390/metabo12030253. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35323696 Free PMC article.
-
A guide to the metabolic pathways and function of metabolites observed in human brain 1H magnetic resonance spectra.Neurochem Res. 2014 Jan;39(1):1-36. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1199-5. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24258018 Review.
-
1H-MRS assessment of the therapeutic effect of bilateral intraventricular BDNF infusion into APP/PS1 double transgenic mice.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Jul;50(3):434-42. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-9951-5. Epub 2013 Jan 15. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23315172
-
Cyclitols: From Basic Understanding to Their Association with Neurodegeneration.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 23;15(9):2029. doi: 10.3390/nu15092029. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium/myo-Inositol transporters: substrate transport requirements and regional brain expression in the TgCRND8 mouse model of amyloid pathology.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024032. Epub 2011 Aug 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brand A, Richter-Landsberg C, Leibfritz D. Multinuclear NMR studies on the energy metabolism of glial and neuronal cells. Dev Neurosci. 1993;15:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Choi JK, Dedeoglu A, Jenkins BG. Application of MRS to mouse models of neurodegenerative illness. NMR Biomed. 2007;20:216–237. - PubMed
-
- Dedeoglu A, Choi JK, Cormier K, Kowall NW, Jenkins BG. Magnetic resonance spectroscopic analysis of Alzheimer's disease mouse brain that express mutant human APP shows altered neurochemical profile. Brain Res. 2004;1012:60–65. - PubMed
-
- Dickson DW. The pathogenesis of senile plaques. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997;56:321–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

