A four-kallikrein panel predicts prostate cancer in men with recent screening: data from the European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer, Rotterdam
- PMID: 20400522
- PMCID: PMC2891337
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0122
A four-kallikrein panel predicts prostate cancer in men with recent screening: data from the European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer, Rotterdam
Abstract
Purpose: We have developed a statistical prediction model for prostate cancer based on four kallikrein markers in blood: total, free, and intact prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and kallikrein-related peptidase 2 (hK2). Although this model accurately predicts the result of biopsy in unscreened men, its properties for men with a history of PSA screening have not been fully characterized.
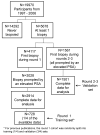
Experimental design: A total of 1,501 previously screened men with elevated PSA underwent initial biopsy during rounds 2 and 3 of the European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer, Rotterdam, with 388 cancers diagnosed. Biomarker levels were measured in serum samples taken before biopsy. The prediction model developed on the unscreened cohort was then applied and predictions compared with biopsy outcome.
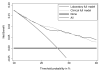
Results: The previously developed four-kallikrein prediction model had much higher predictive accuracy than PSA and age alone (area under the curve of 0.711 versus 0.585, and 0.713 versus 0.557 with and without digital rectal exam, respectively; both P < 0.001). Similar statistically significant enhancements were seen for high-grade cancer. Applying the model with a cutoff of 20% cancer risk as the criterion for biopsy would reduce the biopsy rate by 362 for every 1,000 men with elevated PSA. Although diagnosis would be delayed for 47 cancers, these would be predominately low-stage and low-grade (83% Gleason 6 T(1c)).
Conclusions: A panel of four kallikreins can help predict the result of initial biopsy in previously screened men with elevated PSA. Use of a statistical model based on the panel would substantially decrease rates of unnecessary biopsy.
(c) 2010 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Schroder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ, et al. Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1320–8. - PubMed
-
- Ulmert D, Serio AM, O'Brien MF, et al. Long-term prediction of prostate cancer: prostate-specific antigen (PSA) velocity is predictive but does not improve the predictive accuracy of a single PSA measurement 15 years or more before cancer diagnosis in a large, representative, unscreened population. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:835–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

