Phosphorylation state of the Na+-K+-Cl- cotransporter (NKCC1) in the gills of Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) during acclimation to water of varying salinity
- PMID: 20400641
- PMCID: PMC2856500
- DOI: 10.1242/jeb.039644
Phosphorylation state of the Na+-K+-Cl- cotransporter (NKCC1) in the gills of Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) during acclimation to water of varying salinity
Abstract
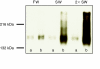
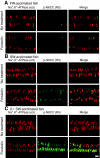
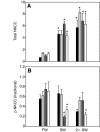
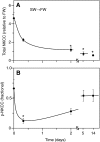
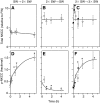
Euryhaline teleosts such as Atlantic killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) are able to acclimate to changing environmental salinity by tightly regulating NaCl absorption and secretion across their gills. Many studies have examined the mechanisms responsible for long-term (days) salinity acclimation; however, much remains unknown about the mechanisms of acute (hours) salinity acclimation. In this study, we tested the hypotheses that phosphorylation of the Na(+)-K(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter (NKCC1) located in the basolateral membrane of the gill plays a role in acute salinity acclimation and that changes in NKCC1 phosphorylation are mediated by a cAMP-protein kinase A (cAMP-PKA) pathway. Using a phospho-specific antibody, we determined the time course of changes in total and phosphorylated NKCC1 protein during acclimation to water of various salinities. Long-term (>or=14 days) acclimation of killifish to seawater (SW) and 2x SW resulted in 4- to 6-fold and 5- to 8-fold increases, respectively, in total gill NKCC1 protein relative to fish maintained in freshwater (FW). NKCC1 was found to be between 20% and 70% activated in fish, with lower average activation in fish acclimated to SW and 2x SW compared with FW fish. Increases and decreases in the fractional level of NKCC1 phosphorylation were seen within 1 h of transfer of fish to water of higher and lower salinity, respectively, consistent with a regulatory role of phosphorylation prior to an increase in the biosynthesis of NKCC1; large changes in protein expression of NKCC1 were observed over periods of hours to days. We found that NKCC1 phosphorylation is acutely regulated in the killifish gill in response to changing environmental salinity and that phosphorylation in excised gills increases in response to forskolin stimulation of the cAMP-PKA pathway. The role of phosphorylation is further underscored by the observation that mRNA expression of sterile 20 (Ste20)-related proline-alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) changes with salinity acclimation, being 2.7-fold greater in SW-acclimated killifish relative to FW fish. Overall, these results demonstrate an important role of NKCC1 phosphorylation in the gill of Atlantic killifish during acute salinity acclimation.
Figures



References
-
- Behnke R. J., Colon D. E., Zadunaisky J. A., Forbush B. (1999). Expression of the secretory Na-K-Cl cotransporter is increased during long term salt adaptation in the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Bull. Mt. Desert Isl. Biol. Lab. Salisb. Cove Maine 38, 85-86
-
- Boucher R. C., Larsen E. H. (1988). Comparison of ion-transport by cultured secretory and absorptive canine airway epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 254, C535-C547 - PubMed
-
- Darman R. B., Forbush B. (2002). A regulatory locus of phosphorylation in the N terminus of the Na-K-Cl cotransporter, NKCC1. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 37542-37550 - PubMed
-
- Darman R. B., Flemmer A., Forbush B. (2001). Modulation of ion transport by direct targeting of protein phosphatase type 1 to the Na-K-Cl cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 34359-34362 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

