Design study of a high-resolution breast-dedicated PET system built from cadmium zinc telluride detectors
- PMID: 20400807
- PMCID: PMC3703459
- DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/9/022
Design study of a high-resolution breast-dedicated PET system built from cadmium zinc telluride detectors
Abstract
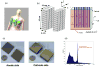
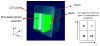
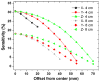
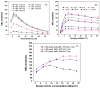
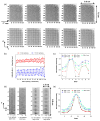
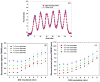
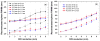
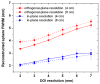
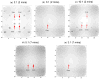
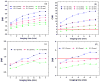
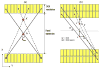
We studied the performance of a dual-panel positron emission tomography (PET) camera dedicated to breast cancer imaging using Monte Carlo simulation. The proposed system consists of two 4 cm thick 12 x 15 cm(2) area cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) panels with adjustable separation, which can be put in close proximity to the breast and/or axillary nodes. Unique characteristics distinguishing the proposed system from previous efforts in breast-dedicated PET instrumentation are the deployment of CZT detectors with superior spatial and energy resolution, using a cross-strip electrode readout scheme to enable 3D positioning of individual photon interaction coordinates in the CZT, which includes directly measured photon depth-of-interaction (DOI), and arranging the detector slabs edge-on with respect to incoming 511 keV photons for high photon sensitivity. The simulation results show that the proposed CZT dual-panel PET system is able to achieve superior performance in terms of photon sensitivity, noise equivalent count rate, spatial resolution and lesion visualization. The proposed system is expected to achieve approximately 32% photon sensitivity for a point source at the center and a 4 cm panel separation. For a simplified breast phantom adjacent to heart and torso compartments, the peak noise equivalent count (NEC) rate is predicted to be approximately 94.2 kcts s(-1) (breast volume: 720 cm(3) and activity concentration: 3.7 kBq cm(-3)) for a approximately 10% energy window around 511 keV and approximately 8 ns coincidence time window. The system achieves 1 mm intrinsic spatial resolution anywhere between the two panels with a 4 cm panel separation if the detectors have DOI resolution less than 2 mm. For a 3 mm DOI resolution, the system exhibits excellent sphere resolution uniformity (sigma(rms)/mean) < or = 10%) across a 4 cm width FOV. Simulation results indicate that the system exhibits superior hot sphere visualization and is expected to visualize 2 mm diameter spheres with a 5:1 activity concentration ratio within roughly 7 min imaging time. Furthermore, we observe that the degree of spatial resolution degradation along the direction orthogonal to the two panels that is typical of a limited angle tomography configuration is mitigated by having high-resolution DOI capabilities that enable more accurate positioning of oblique response lines.
Figures


References
-
- Alessio A, Kinahan P, Cheng P, Vesselle H, Karp J. PET/CT scanner instrumentation, challenges, and solutions. Radiol Clin N Am. 2004;42:1017–32. - PubMed
-
- Avril N, Menzel M, Dose J, Schelling M, Weber W, Jänicke F, Nathrath W, Schwaiger M. Glucose metabolism of breast cancer assessed by 18 F-FDG PET: histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Baghaei H, Wong WH, Uribe J, Li H, Zhang N, Wang Y. Breast cancer studies with a variable field of view PET camera. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2000;47:1080–4.
-
- Baines CJ, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of first screen mammography in the Canadian National Breast Screening Study; a preliminary report from five centers. Radiology. 1986;160:295–8. - PubMed
-
- Barrett HH, Eskin JD, Barber HB. Charge transport in arrays of semiconductor gamma-ray detectors. Phys Rev Lett. 1995;75:156–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
