When tight blood pressure control is not for everyone: a new model for performance measurement in hypertension
- PMID: 20402373
- PMCID: PMC2858350
- DOI: 10.1016/s1553-7250(10)36028-4
When tight blood pressure control is not for everyone: a new model for performance measurement in hypertension
Abstract
Background: Many patients with hypertension have legitimate reasons to forego standard blood pressure targets yet are nonetheless included in performance measurement systems. An approach to performance measurement incorporating clinical reasoning was developed to determine which patients to include in a performance measure.
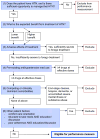
Design: A 10-member multispecialty advisory panel refined a taxonomy of situations in which the balance of benefits and harms of anti-hypertensive treatment does not clearly favor tight blood pressure control (< 140/90 mm Hg).
Findings: The panel identified several broad categories of reasons for exempting a patient from performance measurement for blood pressure control. These included (1) patients who have suffered adverse effects from multiple classes of antihypertensive medications; (2) patients already taking four or more antihypertensive medications; (3) patients with terminal disease, moderate to severe dementia, or other conditions that overwhelmingly dominate the patient's clinical status; and (4) other patient factors, including comfort care orientation and poor medication adherence despite attempts to remedy adherence difficulties. Several general principles also emerged. Performance measurement should focus on patients for whom the benefits of treatment clearly outweigh the harms and should incorporate a longitudinal approach. In addition, the criteria for exempting a patient from performance measurement should be more strict in patients at higher risk of adverse health outcomes from hypertension and more lenient for patients at lower risk.
Conclusions: Incorporating "real world" clinical principles and judgment into performance measurement systems may improve targeting of care and, by accounting for patient case mix, allow for better comparison of performance between institutions.
Figures

References
-
- Walter LC, et al. Pitfalls of converting practice guidelines into quality measures: Lessons learned from a VA performance measure. JAMA. 2004 May 26;291:2466–2470. - PubMed
-
- O’Malley AS, et al. Clinical practice guidelines and performance indicators as related—but often misunderstood—tools. Jt Comm J Qual Saf. 2004 Mar;30:163–171. - PubMed
-
- Kerr EA, et al. Avoiding pitfalls in chronic disease quality measurement: A case for the next generation of technical quality measures. Am J Manag Care. 2001 Nov;7:1033–1043. - PubMed
-
- Hayward RA. Performance measurement in search of a path. N Engl J Med. 2007 Mar 1;356:951–953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

