Signaling pathways controlling the phosphorylation state of WAVE1, a regulator of actin polymerization
- PMID: 20403076
- PMCID: PMC2945298
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06743.x
Signaling pathways controlling the phosphorylation state of WAVE1, a regulator of actin polymerization
Abstract
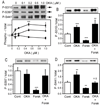
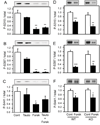
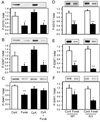
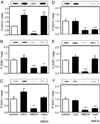
The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)-family verprolin homologous protein 1 (WAVE1) is a key regulator of Arp (actin-related protein) 2/3 complex-mediated actin polymerization. We have established previously that the state of phosphorylation of WAVE1 at three distinct residues controls its ability to regulate actin polymerization and spine morphology. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 phosphorylates WAVE1 at Ser310, Ser397 and Ser441 to a high basal stoichiometry, resulting in inhibition of WAVE1 activity. Our previous and current studies show that WAVE1 can be dephosphorylated at all three sites and thereby activated upon stimulation of the D1 subclass of dopamine receptors and of the NMDA subclass of glutamate receptors, acting through cAMP and Ca(2+) signaling pathways, respectively. Specifically, we have identified protein phosphatase-2A and protein phosphatase-2B as the effectors for these second messengers. These phosphatases act on different sites to mediate receptor-induced signaling pathways, which would lead to activation of WAVE1.
Figures



References
-
- Ardern H, Sandilands E, Machesky LM, Timpson P, Frame MC, Brunton VG. Src-dependent phosphorylation of Scar1 promotes its association with the Arp2/3 complex. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton. 2006;63:6–13. - PubMed
-
- Bibb JA, Snyder GL, Nishi A, Yan Z, Meijer L, Fienberg AA, Tsai LH, Kwon YT, Girault JA, Czernik AJ, Huganir RL, Hemmings HC, Jr, Nairn AC, Greengard P. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 by Cdk5 modulates dopamine signalling in neurons. Nature. 1999;402:669–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

