Curcumin inhibits cholesterol uptake in Caco-2 cells by down-regulation of NPC1L1 expression
- PMID: 20403165
- PMCID: PMC2865464
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-40
Curcumin inhibits cholesterol uptake in Caco-2 cells by down-regulation of NPC1L1 expression
Abstract
Background: Curcumin is a polyphenol and the one of the principle curcuminoids of the spice turmeric. Its antioxidant, anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects have been intensively studied. Previous in vivo studies showed that administration of curcumin also decreased cholesterol levels in the blood, and the effects were considered to be related to upregulation of LDL receptor. However, since plasma cholesterol levels are also influenced by the uptake of cholesterol in the gut, which is mediated by a specific transporter Niemann-Pick Cl-like 1 (NPC1L1) protein, the present study is to investigate whether curcumin affects cholesterol uptake in the intestinal Caco-2 cells.
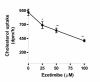
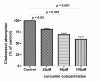
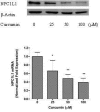
Methods: Caco-2 cells were cultured to confluence. The micelles composed of bile salt, monoolein, and 14C-cholesterol were prepared. We first incubated the cells with the micelles in the presence and absence of ezetimibe, the specific inhibitor of NPC1L1, to see whether the uptake of the cholesterol in the cells was mediated by NPC1L1. We then pretreated the cells with curcumin at different concentrations for 24 h followed by examination of the changes of cholesterol uptake in these curcumin-treated cells. Finally we determined whether curcumin affects the expression of NPC1L1 by both Western blot analysis and qPCR quantification.
Results: We found that the uptake of radioactive cholesterol in Caco-2 cells was inhibited by ezetimibe in a dose-dependent manner. The results indicate that the uptake of cholesterol in this study was mediated by NPC1L1. We then pretreated the cells with 25-100 muM curcumin for 24 h and found that such a treatment dose-dependently inhibited cholesterol uptake with 40% inhibition obtained by 100 muM curcumin. In addition, we found that the curcumin-induced inhibition of cholesterol uptake was associated with significant decrease in the levels of NPC1L1 protein and NPC1L1 mRNA, as analyzed by Western blot and qPCR, respectively.
Conclusion: Curcumin inhibits cholesterol uptake through suppression of NPC1L1 expression in the intestinal cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SREBP2 mediates the modulation of intestinal NPC1L1 expression by curcumin.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):G148-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00119.2011. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21527728 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthohumol Suppresses NPC1L1 Gene Expression through Downregulation of HNF-4α and Inhibits Cholesterol Uptake in Caco-2 Cells.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Oct 9;67(40):11119-11128. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05221. Epub 2019 Sep 26. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 31525874
-
Luteolin and quercetin affect the cholesterol absorption mediated by epithelial cholesterol transporter niemann-pick c1-like 1 in caco-2 cells and rats.PLoS One. 2014 May 23;9(5):e97901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097901. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24859282 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 (NPC1L1) an intestinal sterol transporter.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jul;1791(7):679-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.01.002. Epub 2009 Jan 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19272334 Review.
-
The Effect of Polyphenols on Hypercholesterolemia through Inhibiting the Transport and Expression of Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 6;20(19):4939. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194939. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31590417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactivity of Dietary Polyphenols: The Role in LDL-C Lowering.Foods. 2021 Nov 2;10(11):2666. doi: 10.3390/foods10112666. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34828946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lupin protein isolate versus casein modifies cholesterol excretion and mRNA expression of intestinal sterol transporters in a pig model.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014 Feb 3;11(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-11-9. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014. PMID: 24490902 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of efficacy of curcumin on neurodegeneration in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C1.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Mar;101(1):125-31. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.12.009. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 22202649 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Molecular Mechanisms and Beneficial Effects of Phytochemicals and Plant-Based Whole Foods in Reducing LDL-C and Preventing Cardiovascular Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 15;10(5):784. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050784. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Curcumin in Improving Lipid Profile in Patients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1291:165-177. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-56153-6_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34331690
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

