Cell-specific expression of tryptophan decarboxylase and 10-hydroxygeraniol oxidoreductase, key genes involved in camptothecin biosynthesis in Camptotheca acuminata Decne (Nyssaceae)
- PMID: 20403175
- PMCID: PMC3095343
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-69
Cell-specific expression of tryptophan decarboxylase and 10-hydroxygeraniol oxidoreductase, key genes involved in camptothecin biosynthesis in Camptotheca acuminata Decne (Nyssaceae)
Abstract
Background: Camptotheca acuminata is a major natural source of the terpenoid indole alkaloid camptothecin (CPT). At present, little is known about the cellular distribution of the biosynthesis of CPT, which would be useful knowledge for developing new strategies and technologies for improving alkaloid production.
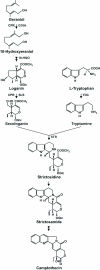
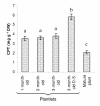
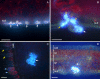
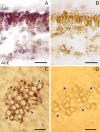
Results: The pattern of CPT accumulation was compared with the expression pattern of some genes involved in CPT biosynthesis in C. acuminata [i.e., Ca-TDC1 and Ca-TDC2 (encoding for tryptophan decarboxylase) and Ca-HGO (encoding for 10-hydroxygeraniol oxidoreductase)]. Both CPT accumulation and gene expression were investigated in plants at different degrees of development and in plantlets subjected to drought-stress. In all organs, CPT accumulation was detected in epidermal idioblasts, in some glandular trichomes, and in groups of idioblast cells localized in parenchyma tissues. Drought-stress caused an increase in CPT accumulation and in the number of glandular trichomes containing CPT, whereas no increase in epidermal or parenchymatous idioblasts was observed. In the leaf, Ca-TDC1 expression was detected in some epidermal cells and in groups of mesophyll cells but not in glandular trichomes; in the stem, it was observed in parenchyma cells of the vascular tissue; in the root, no expression was detected. Ca-TDC2 expression was observed exclusively in leaves of plantlets subjected to drought-stress, in the same sites described for Ca-TDC1. In the leaf, Ca-HGO was detected in all chlorenchyma cells; in the stem, it was observed in the same sites described for Ca-TDC1; in the root, no expression was detected.
Conclusions: The finding that the sites of CPT accumulation are not consistently the same as those in which the studied genes are expressed demonstrates an organ-to-organ and cell-to-cell translocation of CPT or its precursors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pyrosequencing of the Camptotheca acuminata transcriptome reveals putative genes involved in camptothecin biosynthesis and transport.BMC Genomics. 2011 Oct 30;12:533. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-533. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22035094 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular localisation of the anti-cancer drug camptothecin in Camptotheca acuminata Decne (Nyssaceae).Eur J Histochem. 2004 Jul-Sep;48(3):321-7. Eur J Histochem. 2004. PMID: 15596415
-
Tryptophan decarboxylase is encoded by two autonomously regulated genes in Camptotheca acuminata which are differentially expressed during development and stress.Plant J. 1997 Jun;11(6):1167-75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1997.11061167.x. Plant J. 1997. PMID: 9225462
-
Biotechnology of camptothecin production in Nothapodytes nimmoniana, Ophiorrhiza sp. and Camptotheca acuminata.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Dec;105(24):9089-9102. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11700-5. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34850279 Review.
-
Biotechnological approaches for the production of camptothecin.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 19;108(1):382. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13187-2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38896329 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Tryptophan decarboxylase 1 Gene From Aegilops variabilis No.1 Regulate the Resistance Against Cereal Cyst Nematode by Altering the Downstream Secondary Metabolite Contents Rather Than Auxin Synthesis.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Sep 4;9:1297. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01297. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30233630 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrosequencing of the Camptotheca acuminata transcriptome reveals putative genes involved in camptothecin biosynthesis and transport.BMC Genomics. 2011 Oct 30;12:533. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-533. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22035094 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into Catalpol Biosynthesis in the Medicinal Plant Rehmannia glutinosa and the Functional Characterization of RgGES Genes.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 24;15(2):155. doi: 10.3390/genes15020155. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397145 Free PMC article.
-
An ABCG-Type Transporter Facilitates ABA Influx and Regulates Camptothecin Biosynthesis in Camptotheca acuminata.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 17;23(24):16120. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416120. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555760 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and transcriptional analyses in response to potent inhibitors establish MEP pathway as major route for camptothecin biosynthesis in Nothapodytes nimmoniana (Graham) Mabb.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Jul 10;19(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1912-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31291885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wall ME, Wani MC, Cook CE, Palmer KH, McPhail AT, Sim GA. Plant anti-tumor agents. I. The isolation and structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor inhibitor from Camptotheca acuminata. J Am Chem Soc. 1966;88:4888–4890. doi: 10.1021/ja00968a057. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

