Use of kilovoltage X-ray volume imaging in patient dose calculation for head-and-neck and partial brain radiation therapy
- PMID: 20403191
- PMCID: PMC2874569
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-29
Use of kilovoltage X-ray volume imaging in patient dose calculation for head-and-neck and partial brain radiation therapy
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the accuracy of using kilovoltage x-ray cone-beam computed tomography (kV-CBCT) imaging for in vivo dose calculations.
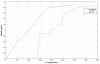
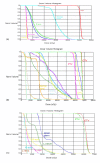
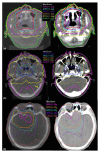
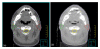
Methods: A Region-of-Interest (ROI) CT number mapping method was developed to generate the cone-beam CT number vs. relative electron density calibration curve for 3D dose calculations. The stability of the results was validated for three consecutive months. The method was evaluated on three brain tumors and three head-and-neck tumor cases. For each patient, kV-CBCT images were acquired on the first treatment day and two-week intervals on the Elekta XVI system. The delivered dose distributions were calculated by applying the patients' treatment plans to the kV-CBCT images. The resulting dose distributions and dose volume histograms (DVHs) of the tumor and critical structures were compared to the original treatment plan.
Results: The kV-CBCT electron density calibration was stable within 1.5% over a three-month period. The DVH and dose distribution comparison based on the planning CT and the initial kV-CBCT showed good agreements for majority of cases. The doses calculated from the planning CT and kV-CBCT were compared on planes perpendicular to the beam axes and passing through the isocenter. Using gamma analysis with a criterion of 2 mm/2% and a threshold of 10%, more than 99.5% of the points on the iso-planes exhibited gamma <1. For one patient, kV-CBCT images detected 5.8% dose variation in the right parotid due to tumor shrinkage and patient weight loss.
Conclusions: ROI mapping method is an effective method for the creation of kV-CBCT electron density calibration curves for head-and-neck and brain tumor patients. Dose variations as monitored using kV-CBCT imaging suggest that some patients can benefit from adaptive treatment plan re-optimization.
Figures
References
-
- Hong TS, Tomé WA, Chappell RJ, Chinnaiyan P, Mehta MP, Harari PM. The impact of daily setup variations on head-and-neck intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61:779–88. - PubMed
-
- Han C, Chen YJ, Liu A, Schultheiss TE, Wong JY. Actual dose variation of parotid glands and spinal cord for nasopharyngeal cancer patients during radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:1256–62. - PubMed
-
- Barker JL Jr, Garden AS, Ang KK, O'Daniel JC, Wang H, Court LE, Morrison WH, Rosenthal DI, Chao KS, Tucker SL, Mohan R, Dong L. Quantification of volumetric and geometric changes occurring during fractionated radiotherapy for head-and-neck cancer using an integrated CT/linear accelerator system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59:960–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.12.024. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

