Role of myosin light chain kinase in intestinal epithelial barrier defects in a rat model of bowel obstruction
- PMID: 20403206
- PMCID: PMC2868795
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-39
Role of myosin light chain kinase in intestinal epithelial barrier defects in a rat model of bowel obstruction
Abstract
Background: Bowel obstruction is a common cause of abdominal emergency, since the patients are at increased risk of septicemia resulting in high mortality rate. While the compartmentalized changes in enteric microfloral population and augmentation of bacterial translocation (BT) have already been reported using experimental obstruction models, alterations in epithelial permeability of the obstructed guts has not been studied in detail. Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is actively involved in the contraction of epithelial perijunctional actinomyosin ring and thereby increases paracellular permeability. In the current study we attempt to investigate the role of MLCK in epithelial barrier defects using a rat model of simple mechanical obstruction.
Methods: Wistar rats received intraperitoneal injection of ML-7 (a MLCK inhibitor) or vehicle at 24, 12 and 1 hrs before and 12 hrs after intestinal obstruction (IO). The distal small intestine was obstructed with a single ligature placed 10 cm proximal to the ileocecal junction in IO rats for 24 hrs. Sham-operated rats served as controls.
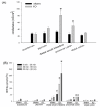
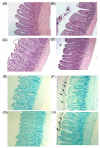
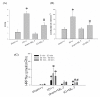
Results: Mucosal injury, such as villous blunting and increased crypt/villus ratio, was observed in the distal small intestine of IO rats. Despite massive enterocyte shedding, intestinal villi were covered with a contiguous epithelial layer without cell apoptosis. Increased transmural macromolecular flux was noticed in the distal small intestine and the proximal colon after IO. The bacterial colony forming units in the spleen and liver of IO rats were significantly higher than those of sham controls. Addition of ML-7 ameliorated the IO-triggered epithelial MLC phosphorylation, mucosal injury and macromolecular flux, but not the level of BT.
Conclusions: The results suggest that IO-induced premature enterocytic sloughing and enhanced paracellular antigenic flux were mediated by epithelial MLCK activation. In addition, enteric bacteria may undergo transcytotic routes other than paracellular paths to cross the epithelium.
Figures

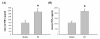



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

