Reconstitution of the RIG-I pathway reveals a signaling role of unanchored polyubiquitin chains in innate immunity
- PMID: 20403326
- PMCID: PMC2919214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.029
Reconstitution of the RIG-I pathway reveals a signaling role of unanchored polyubiquitin chains in innate immunity
Abstract
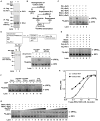
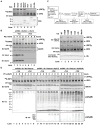
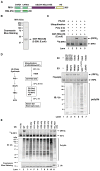
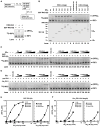
RIG-I detects invading viral RNA and activates the transcription factors NF-kappaB and IRF3 through the mitochondrial protein MAVS. Here we show that RNA bearing 5'-triphosphate strongly activates the RIG-I-IRF3 signaling cascade in a reconstituted system composed of RIG-I, mitochondria, and cytosol. Activation of RIG-I requires not only RNA but also polyubiquitin chains linked through lysine 63 (K63) of ubiquitin. RIG-I binds specifically to K63-polyubiquitin chains through its tandem CARD domains in a manner that depends on RNA and ATP. Mutations in the CARD domains that abrogate ubiquitin binding also impair RIG-I activation. Remarkably, unanchored K63-ubiquitin chains, which are not conjugated to any target protein, potently activate RIG-I. These ubiquitin chains function as an endogenous ligand of RIG-I in human cells. Our results delineate the mechanism of RIG-I activation, identify CARD domains as a ubiquitin sensor, and demonstrate that unanchored K63-polyubiquitin chains are signaling molecules in antiviral innate immunity.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Ubiquitin gets CARDed.Cell. 2010 Apr 16;141(2):220-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.047. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20403317
-
Innate immunity: A chain reaction.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Jun;10(6):385. doi: 10.1038/nri2783. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20514677 No abstract available.
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Bhoj VG, Chen ZJ. Ubiquitylation in innate and adaptive immunity. Nature. 2009;458:430–437. - PubMed
-
- Cui S, Eisenacher K, Kirchhofer A, Brzozka K, Lammens A, Lammens K, Fujita T, Conzelmann KK, Krug A, Hopfner KP. The C-terminal regulatory domain is the RNA 5′-triphosphate sensor of RIG-I. Mol Cell. 2008;29:169–179. - PubMed
-
- Deng L, Wang C, Spencer E, Yang L, Braun A, You J, Slaughter C, Pickart C, Chen ZJ. Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell. 2000;103:351–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

