Validation of a modified method for Bxb1 mycobacteriophage integrase-mediated recombination in Plasmodium falciparum by localization of the H-protein of the glycine cleavage complex to the mitochondrion
- PMID: 20403390
- PMCID: PMC2875341
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2010.04.005
Validation of a modified method for Bxb1 mycobacteriophage integrase-mediated recombination in Plasmodium falciparum by localization of the H-protein of the glycine cleavage complex to the mitochondrion
Abstract
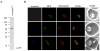
The glycine cleavage complex (GCV) is a potential source of the one carbon donor 5,10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH(2)-THF) in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. One carbon (C1) donor units are necessary for amino acid and nucleotide biosynthesis, and for the initiation of mitochondrial and plastid translation. In other organisms, GCV activity is closely coordinated with the activity of serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) enzymes. P. falciparum contains cytosolic and mitochondrial SHMT isoforms, and thus, the subcellular location of the GCV is an important indicator of its role in malaria metabolism. To determine the subcellular localization of the GCV, we used a modified version of the published method for mycobacteriophage integrase-mediated recombination in P. falciparum to generate cell lines containing one of the component proteins of the GCV, the H-protein, fused to GFP. Here, we demonstrate that this modification results in rapid generation of chromosomally integrated transgenic parasites, and we show that the H-protein localizes to the mitochondrion.
Figures

References
-
- Motokawa Y, Kikuchi G. Glycine metabolism by rat liver mitochondria. Isolation and some properties of the protein-bound intermediate of the reversible glycine cleavage reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974;164:634–40. - PubMed
-
- Douce R, Bourguignon J, Neuburger M, Rebeille F. The glycine decarboxylase system: a fascinating complex. Trends Plant Sci. 2001;6:167–76. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara K, Motokawa Y. Mechanism of the glycine cleavage reaction. Steady state kinetic studies of the P-protein-catalyzed reaction. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:8156–62. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara K, Okamura-Ikeda K, Ohmura Y, Motokawa Y. Mechanism of the glycine cleavage reaction: retention of C-2 hydrogens of glycine on the intermediate attached to H-protein and evidence for the inability of serine hydroxymethyltransferase to catalyze the glycine decarboxylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986;251:121–7. - PubMed
-
- Okamura-Ikeda K, Fujiwara K, Motokawa Y. Purification and characterization of chicken liver T-protein, a component of the glycine cleavage system. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:135–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

