Strigolactones as germination stimulants for root parasitic plants
- PMID: 20403809
- PMCID: PMC2900819
- DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcq055
Strigolactones as germination stimulants for root parasitic plants
Abstract
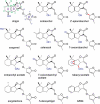
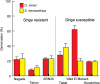
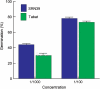
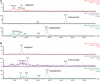
Witchweeds (Striga spp.) and broomrapes (Orobanche and Phelipanche spp.) are the two most devastating root parasitic plants belonging to the family Orobanchaceae and are causing enormous crop losses throughout the world. Seeds of these root parasites will not germinate unless they are exposed to chemical stimuli, 'germination stimulants' produced by and released from plant roots. Most of the germination stimulants identified so far are strigolactones (SLs), which also function as host recognition signals for arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and a novel class of plant hormones inhibiting shoot branching. In this review, we focus on SLs as germination stimulants for root parasitic plants. In addition, we discuss how quantitative and qualitative differences in SL exudation among sorghum cultivars influence their susceptibility to Striga.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyama K., Matsuzaki K., Hayashi H. Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature. 2005;435:824–827. - PubMed
-
- Awad A.A., Sato D., Kusumoto D., Kamioka H., Takeuchi Y., Yoneyama K. Characterization of strigolactones, germination stimulants for the root parasitic plants Striga and Orobanche, produced by maize, millet and sorghum. Plant Growth Regul. 2006;48:221–227.
-
- Bouwmeester H.J., Matusova R., Zhongkui S., Beale M.H. Secondary metabolite signalling in host–parasitic plant interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003;6:358–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

