Androgens and spermatogenesis: lessons from transgenic mouse models
- PMID: 20403868
- PMCID: PMC2871915
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0117
Androgens and spermatogenesis: lessons from transgenic mouse models
Abstract
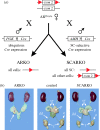
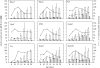
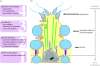
Transgenic mouse models have contributed considerably to our understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which androgens control spermatogenesis. Cell-selective ablation of the androgen receptor (AR) in Sertoli cells (SC) results in a complete block in meiosis and unambiguously identifies the SC as the main cellular mediator of the effects of androgens on spermatogenesis. This conclusion is corroborated by similar knockouts in other potential testicular target cells. Mutations resulting in diminished expression of the AR or in alleles with increased length of the CAG repeat mimick specific human forms of disturbed fertility that are not accompanied by defects in male sexual development. Transcriptional profiling studies in mice with cell-selective and general knockouts of the AR, searching for androgen-regulated genes relevant to the control of spermatogenesis, have identified many candidate target genes. However, with the exception of Rhox5, the identified subsets of genes show little overlap. Genes related to tubular restructuring, cell junction dynamics, the cytoskeleton, solute transportation and vitamin A metabolism are prominently present. Further research will be needed to decide which of these genes are physiologically relevant and to identify genes that can be used as diagnostic tools or targets to modulate the effects of androgens in spermatogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Abel M. H., Wootton A. N., Wilkins V., Huhtaniemi I., Knight P. G., Charlton H. M.2000The effect of a null mutation in the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor gene on mouse reproduction. Endocrinology 141, 1795–1803 (doi:10.1210/en.141.5.1795) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abel M. H., Baker P. J., Charlton H. M., Monteiro A., Verhoeven G., De Gendt K., Guillou F., O'Shaughnessy P. J.2008Spermatogenesis and Sertoli cell activity in mice lacking Sertoli cell receptors for follicle-stimulating hormone and androgen. Endocrinology 149, 3279–3285 (doi:10.1210/en.2008-0086) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allan C. M., et al. 2001A novel transgenic model to characterize the specific effects of follicle-stimulating hormone on gonadal physiology in the absence of luteinizing hormone actions. Endocrinology 142, 2213–2220 (doi:10.1210/en.142.6.2213) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Au C. L., Irby D. C., Robertson D. M., deKretser D. M.1986Effects of testosterone on testicular inhibin and fluid production in intact and hypophysectomized adult-rats. J. Reprod. Fertil. 76, 257–266 - PubMed
-
- Barbulescu K., Geserick C., Schuttke I., Schleuning W. D., Haendler B.2001New androgen response elements in the murine Pem promoter mediate selective transactivation. Mol. Endocrinol. 15, 1803–1816 (doi:10.1210/me.15.10.1803) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
