{beta}-Apocarotenoids do not significantly activate retinoic acid receptors {alpha} or {beta}
- PMID: 20404052
- PMCID: PMC3526007
- DOI: 10.1258/ebm.2009.009202
{beta}-Apocarotenoids do not significantly activate retinoic acid receptors {alpha} or {beta}
Abstract
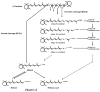
beta-Carotene oxygenase 2 cleaves beta-carotene asymmetrically at non-central double bonds of the polyene chain, yielding apocarotenal molecules. The hypothesis tested was that apocarotenoids are able to stimulate transcription by activating retinoic acid receptors (RARs). The effects of long- and short-chain apocarotenals and apocarotenoic acids on the activation of RARalpha and RARbeta transfected into monkey kidney fibroblast cells (CV-1) were investigated. We synthesized or purified beta-apo-8'-carotenoic acid (apo-8'-CA), beta-apo-14'-carotenoic acid (apo-14'-CA), beta-cyclocitral (BCL), beta-cyclogernanic acid (BCA), beta-ionone (BI), beta-ionylideneacetaldehyde (BIA) beta-ionylideneacetic acid (BIAA) and a C13 ketone, beta-apo-13-carotenone (C13). None of the apocarotenoids tested showed significant transactivation activity for the RARs when compared with all-trans retinoic acid (RA). The results suggest that biological effects of these apocarotenoids are through mechanisms other than activation of RARalpha and beta.
Figures




References
-
- Goodwin TW. Metabolism, nutrition and function of carotenoids. Annu Rev Nut. 1986;6:273–97. - PubMed
-
- Packer L. The Antioxidant Miracle. The Controversial Carotenoids. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2000. pp. 133–41.
-
- Bieri JG, Brown ED, Smith JC. Determination of individual carotenoids in human plasma by high peformance liquid chromatography. J Liq Chromatogr. 1985;8:473–84.
-
- Olson JA. The effect of bile and bile salts on the uptake and cleavage of β-carotene into retinol ester (vitamin A ester) by intestinal slices. J Lipid Res. 1964;5:402–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

