Lin9, a subunit of the mammalian DREAM complex, is essential for embryonic development, for survival of adult mice, and for tumor suppression
- PMID: 20404087
- PMCID: PMC2876665
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00028-10
Lin9, a subunit of the mammalian DREAM complex, is essential for embryonic development, for survival of adult mice, and for tumor suppression
Abstract
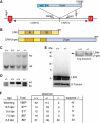
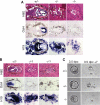
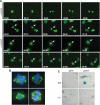
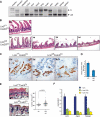
The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (pRB) and related p107 and p130 "pocket proteins" function together with the E2F transcription factors to repress gene expression during the cell cycle and development. Recent biochemical studies have identified the multisubunit DREAM pocket protein complexes in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans in regulating developmental gene repression. Although a conserved DREAM complex has also been identified in mammalian cells, its physiological function in vivo has not been determined. Here we addressed this question by targeting Lin9, a conserved core subunit of DREAM. We found that LIN9 is essential for early embryonic development and for viability of adult mice. Loss of Lin9 abolishes proliferation and leads to multiple defects in mitosis and cytokinesis because of its requirement for the expression of a large set of mitotic genes, such as Plk1, Aurora A, and Kif20a. While Lin9 heterozygous mice are healthy and normal, they are more susceptible to lung tumorigenesis induced by oncogenic c-Raf than wild-type mice. Together these experiments provide the first direct genetic evidence for the role of LIN9 in development and mitotic gene regulation and they suggest that it may function as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor.
Figures



References
-
- Beitel, G. J., E. J. Lambie, and H. R. Horvitz. 2000. The C. elegans gene lin-9, which acts in an Rb-related pathway, is required for gonadal sheath cell development and encodes a novel protein. Gene 254:253-263. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, B. E., M. Kamal, K. Lindblad-Toh, S. Bekiranov, D. K. Bailey, D. J. Huebert, S. McMahon, E. K. Karlsson, E. J. Kulbokas, 3rd, T. R. Gingeras, S. L. Schreiber, and E. S. Lander. 2005. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell 120:169-181. - PubMed
-
- Cotsiki, M., R. L. Lock, Y. Cheng, G. L. Williams, J. Zhao, D. Perera, R. Freire, A. Entwistle, E. A. Golemis, T. M. Roberts, P. S. Jat, and O. V. Gjoerup. 2004. Simian virus 40 large T antigen targets the spindle assembly checkpoint protein Bub1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101:947-952. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
