Antigen affinity discrimination is an intrinsic function of the B cell receptor
- PMID: 20404102
- PMCID: PMC2867278
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20092123
Antigen affinity discrimination is an intrinsic function of the B cell receptor
Abstract
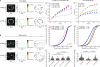
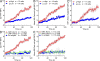
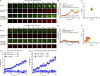
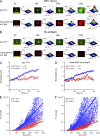
Antibody affinity maturation, a hallmark of adaptive immune responses, results from the selection of B cells expressing somatically hypermutated B cell receptors (BCRs) with increased affinity for antigens. Despite the central role of affinity maturation in antibody responses, the molecular mechanisms by which the increased affinity of a B cell for antigen is translated into a selective advantage for that B cell in immune responses is incompletely understood. We use high resolution live-cell imaging to provide evidence that the earliest BCR-intrinsic events that follow within seconds of BCR-antigen binding are highly sensitive to the affinity of the BCR for antigen. High affinity BCRs readily form oligomers and the resulting microclusters grow rapidly, resulting in enhanced recruitment of Syk kinase and calcium fluxes. Thus, B cells are able to read the affinity of antigen by BCR-intrinsic mechanisms during the earliest phases of BCR clustering, leading to the initiation of B cell responses.
Figures
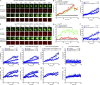
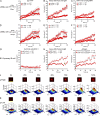
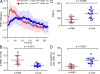
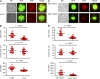

Comment in
-
Affinity measured by microcluster.J Exp Med. 2010 May 10;207(5):907-9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100780. Epub 2010 May 3. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20439542 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
The tipping points in the initiation of B cell signalling: how small changes make big differences.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Nov;10(11):767-77. doi: 10.1038/nri2853. Epub 2010 Oct 11. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20935671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsic differences in the initiation of B cell receptor signaling favor responses of human IgG(+) memory B cells over IgM(+) naive B cells.J Immunol. 2012 Apr 1;188(7):3332-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102322. Epub 2012 Feb 29. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22379037 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic properties of immunoglobulin IgG1 isotype-switched B cell receptors promote microclustering and the initiation of signaling.Immunity. 2010 Jun 25;32(6):778-89. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.06.006. Immunity. 2010. PMID: 20620943 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane heterogeneities in the formation of B cell receptor-Lyn kinase microclusters and the immune synapse.J Cell Biol. 2008 Jul 28;182(2):367-79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200802007. Epub 2008 Jul 21. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18644892 Free PMC article.
-
Control of memory B cell responses by extrinsic and intrinsic mechanisms.Immunol Lett. 2016 Oct;178:27-30. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Immunol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27345519 Review.
Cited by
-
Etiopathogenesis of insulin autoimmunity.Anat Res Int. 2012;2012:457546. doi: 10.1155/2012/457546. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Anat Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22567309 Free PMC article.
-
Fc receptor-like 1 intrinsically recruits c-Abl to enhance B cell activation and function.Sci Adv. 2019 Jul 17;5(7):eaaw0315. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw0315. eCollection 2019 Jul. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31328160 Free PMC article.
-
Acidic phospholipids govern the enhanced activation of IgG-B cell receptor.Nat Commun. 2015 Oct 6;6:8552. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9552. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26440273 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate stiffness governs the initiation of B cell activation by the concerted signaling of PKCβ and focal adhesion kinase.Elife. 2017 Jul 31;6:e23060. doi: 10.7554/eLife.23060. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28755662 Free PMC article.
-
Traction Force Microscopy for Studying B Lymphocyte Mechanosensing.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2909:63-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4442-3_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40029515
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

