Rho1 regulates apoptosis via activation of the JNK signaling pathway at the plasma membrane
- PMID: 20404112
- PMCID: PMC2856900
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200912010
Rho1 regulates apoptosis via activation of the JNK signaling pathway at the plasma membrane
Abstract
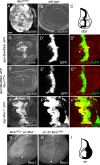
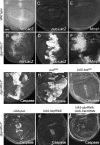
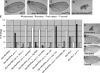
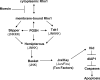
Precisely controlled growth and morphogenesis of developing epithelial tissues require coordination of multiple factors, including proliferation, adhesion, cell shape, and apoptosis. RhoA, a small GTPase, is known to control epithelial morphogenesis and integrity through its ability to regulate the cytoskeleton. In this study, we examine a less well-characterized RhoA function in cell survival. We demonstrate that the Drosophila melanogaster RhoA, Rho1, promotes apoptosis independently of Rho kinase through its effects on c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling. In addition, Rho1 forms a complex with Slipper (Slpr), an upstream activator of the JNK pathway. Loss of Moesin (Moe), an upstream regulator of Rho1 activity, results in increased levels of Rho1 at the plasma membrane and cortical accumulation of Slpr. Together, these results suggest that Rho1 functions at the cell cortex to regulate JNK activity and implicate Rho1 and Moe in epithelial cell survival.
Figures



References
-
- Afshar K., Stuart B., Wasserman S.A. 2000. Functional analysis of the Drosophila diaphanous FH protein in early embryonic development. Development. 127:1887–1897 - PubMed
-
- Agnès F., Suzanne M., Noselli S. 1999. The Drosophila JNK pathway controls the morphogenesis of imaginal discs during metamorphosis. Development. 126:5453–5462 - PubMed
-
- Bloor J.W., Kiehart D.P. 2002. Drosophila RhoA regulates the cytoskeleton and cell-cell adhesion in the developing epidermis. Development. 129:3173–3183 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

