Prophylactic activity of intramuscular peramivir in mice infected with a recombinant influenza A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus containing the H274Y neuraminidase mutation
- PMID: 20404128
- PMCID: PMC2897313
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01681-09
Prophylactic activity of intramuscular peramivir in mice infected with a recombinant influenza A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus containing the H274Y neuraminidase mutation
Abstract
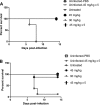
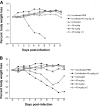
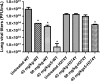
Peramivir is a neuraminidase (NA) inhibitor (NAI) under development that must be administered by the systemic route. The prophylactic activity of intramuscular (IM) peramivir was evaluated with mice infected with wild-type (WT) and oseltamivir-resistant (H274Y NA mutant) recombinant influenza A/WSN/33 (H1N1) viruses. Treatment regimens consisted of IM injections starting 1 h before viral challenge that were single (45 mg/kg or 90 mg/kg) or multiple (45 mg/kg daily for 5 days). All peramivir regimens prevented mortality and weight loss while significantly reducing lung viral titers (LVT) in mice infected with the WT virus. For animals infected with the H274Y mutant, the multiple-dose regimen completely prevented mortality and was associated with significant reduction in weight loss and LVT compared to untreated animals. In contrast, both single-treatment regimens reduced mortality and weight loss but did not significantly reduce LVT. Although further experiments using different influenza A/H1N1 virus strains and other animal models are needed, our results suggest that 5-day IM peramivir therapy may be considered a prophylactic alternative to control influenza infections caused by oseltamivir-resistant viruses with the H274Y mutation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic activity of intramuscular peramivir in mice infected with a recombinant influenza A/WSN/33 (H1N1) virus containing the H275Y neuraminidase mutation.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Aug;56(8):4375-80. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00753-12. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22664977 Free PMC article.
-
Combinations of oseltamivir and peramivir for the treatment of influenza A (H1N1) virus infections in cell culture and in mice.Antiviral Res. 2010 Oct;88(1):38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.07.003. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Antiviral Res. 2010. PMID: 20633577 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-influenza virus activity of peramivir in mice with single intramuscular injection.Antiviral Res. 2006 Jan;69(1):39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2005.10.002. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Antiviral Res. 2006. PMID: 16325932
-
Peramivir: an intravenous neuraminidase inhibitor for the treatment of 2009 H1N1 influenza.Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Jul-Aug;44(7-8):1240-9. doi: 10.1345/aph.1P031. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20516360 Review.
-
[Peramivir. A new and potent neuraminidase inhibitor for the treatment of influenza].Rev Esp Quimioter. 2006 Dec;19(4):317-22. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2006. PMID: 17235399 Review. Spanish. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Generation and characterization of recombinant pandemic influenza A(H1N1) viruses resistant to neuraminidase inhibitors.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jan 1;203(1):25-31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq010. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21148493 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of mutations at residue I223 of the neuraminidase protein on the resistance profile, replication level, and virulence of the 2009 pandemic influenza virus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Mar;56(3):1208-14. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05994-11. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22203589 Free PMC article.
-
PA and PA-X: two key proteins from segment 3 of the influenza viruses.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Mar 14;15:1560250. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1560250. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40160474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peramivir: A Novel Intravenous Neuraminidase Inhibitor for Treatment of Acute Influenza Infections.Front Microbiol. 2016 Mar 31;7:450. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00450. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27065996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influenza antivirals and animal models.FEBS Open Bio. 2022 Jun;12(6):1142-1165. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13416. Epub 2022 Apr 27. FEBS Open Bio. 2022. PMID: 35451200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abed, Y., N. Goyette, and G. Boivin. 2004. A reverse genetics study of resistance to neuraminidase inhibitors in an influenza A/H1N1 virus. Antivir. Ther. 9:577-581. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, F. Y., G. Boivin, and N. Roberts. 2007. Influenza virus susceptibility and resistance to oseltamivir. Antivir. Ther. 12:603-616. - PubMed
-
- Babu, Y. S., P. Chand, S. Bantia, P. Kotian, A. Dehghani, Y. El-Kattan, T. H. Lin, T. L. Hutchison, A. J. Elliott, C. D. Parker, S. L. Ananth, L. L. Horn, G. W. Laver, and J. A. Montgomery. 2000. BCX-1812 (RWJ-270201): discovery of a novel, highly potent, orally active, and selective influenza neuraminidase inhibitor through structure-based drug design. J. Med. Chem. 43:3482-3486. - PubMed
-
- Bantia, S., C. S. Arnold, C. D. Parker, R. Upshaw, and P. Chand. 2006. Anti-influenza virus activity of peramivir in mice with single intramuscular injection. Antiviral Res. 69:39-45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

