IL-23 suppresses innate immune response independently of IL-17A during carcinogenesis and metastasis
- PMID: 20404142
- PMCID: PMC2889517
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003251107
IL-23 suppresses innate immune response independently of IL-17A during carcinogenesis and metastasis
Abstract
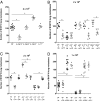
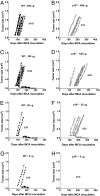
IL-23 is an important molecular driver of Th17 cells and has strong tumor-promoting proinflammatory activity postulated to occur via adaptive immunity. Conversely, more recently it has been reported that IL-17A elicits a protective inflammation that promotes the activation of tumor-specific CD8(+) T cells. Here we show the much broader impact of IL-23 in antagonizing antitumor immune responses primarily mediated by innate immunity. Furthermore, the majority of this impact was independent of IL-17A, which did not appear critical for many host responses to tumor initiation or metastases. IL-23-deficient mice were resistant to experimental tumor metastases in three models where host NK cells controlled disease. Immunotherapy with IL-2 was more effective in mice lacking IL-23, and again the protection afforded was NK cell mediated and independent of IL-17A. Further investigation revealed that loss of IL-23 promoted perforin and IFN-gamma antitumor effector function in both metastasis models examined. IL-23-deficiency also strikingly protected mice from tumor formation in two distinct mouse models of carcinogenesis where the dependence on host IL-12p40 and IL-17A was quite different. Notably, in the 3'-methylcholanthrene (MCA) induction of fibrosarcoma model, this protection was completely lost in the absence of NK cells. Overall, these data indicate the general role that IL-23 plays in suppressing natural or cytokine-induced innate immunity, promoting tumor development and metastases independently of IL-17A.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors M.J.S. and M.W.L.T. declare a conflict of interest. AMGEN Inc. has in part supported the work in this manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Production of IL-17A at Innate Immune Phase Leads to Decreased Th1 Immune Response and Attenuated Host Defense against Infection with Cryptococcus deneoformans.J Immunol. 2020 Aug 1;205(3):686-698. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901238. Epub 2020 Jun 19. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32561568
-
Resistin-like molecule α promotes pathogenic Th17 cell responses and bacterial-induced intestinal inflammation.J Immunol. 2013 Mar 1;190(5):2292-300. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200706. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23355735 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential cytokine pathways for therapeutic intervention in murine primary biliary cirrhosis.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 10;8(9):e74225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074225. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040208 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 17 is a chief orchestrator of immunity.Nat Immunol. 2017 May 18;18(6):612-621. doi: 10.1038/ni.3742. Nat Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28518156 Review.
-
IL-17A in gastric carcinogenesis: good or bad?Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 29;15:1501293. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501293. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39676857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines: from discovery to targeted therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.Nat Med. 2015 Jul;21(7):719-29. doi: 10.1038/nm.3895. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26121196 Review.
-
Increased Th17 cells in the tumor microenvironment is mediated by IL-23 via tumor-secreted prostaglandin E2.J Immunol. 2013 Jun 1;190(11):5894-902. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203141. Epub 2013 May 3. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23645882 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the role of Samsn1 loss in multiple myeloma development.FASEB Bioadv. 2020 Aug 5;2(9):554-572. doi: 10.1096/fba.2020-00027. eCollection 2020 Sep. FASEB Bioadv. 2020. PMID: 32923989 Free PMC article.
-
The Macrophages-Microbiota Interplay in Colorectal Cancer (CRC)-Related Inflammation: Prognostic and Therapeutic Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 18;21(18):6866. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186866. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32962159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cells require IL-28R for optimal in vivo activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 5;112(18):E2376-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424241112. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25901316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trinchieri G, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA. The IL-12 family of heterodimeric cytokines: New players in the regulation of T cell responses. Immunity. 2003;19:641–644. - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Oppmann B, et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13:715–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

