Domain organization and function in GluK2 subtype kainate receptors
- PMID: 20404149
- PMCID: PMC2889583
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1000838107
Domain organization and function in GluK2 subtype kainate receptors
Abstract
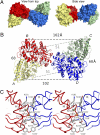
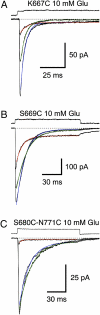
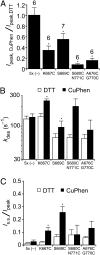
Glutamate receptor ion channels (iGluRs) are excitatory neurotransmitter receptors with a unique molecular architecture in which the extracellular domains assemble as a dimer of dimers. The structure of individual dimer assemblies has been established previously for both the isolated ligand-binding domain (LBD) and more recently for the larger amino terminal domain (ATD). How these dimers pack to form tetrameric assemblies in intact iGluRs has remained controversial. Using recently solved crystal structures for the GluK2 kainate receptor ATD as a guide, we performed cysteine mutant cross-linking experiments in full-length tetrameric GluK2 to establish how the ATD packs in a dimer of dimers assembly. A similar approach, using a full-length AMPA receptor GluA2 crystal structure as a guide, was used to design cysteine mutant cross-links for the GluK2 LBD dimer of dimers assembly. The formation of cross-linked tetramers in full-length GluK2 by combinations of ATD and LBD mutants which individually produce only cross-linked dimers suggests that subunits in the ATD and LBD layers swap dimer partners. Functional studies reveal that cross-linking either the ATD or the LBD inhibits activation of GluK2 and that, in the LBD, cross-links within and between dimers have different effects. These results establish that kainate and AMPA receptors have a conserved extracellular architecture and provide insight into the role of individual dimer assemblies in activation of ion channel gating.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51:7–61. - PubMed
-
- Unwin N. Refined structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at 4A resolution. J Mol Biol. 2005;346:967–989. - PubMed
-
- Hilf RJ, Dutzler R. X-ray structure of a prokaryotic pentameric ligand-gated ion channel. Nature. 2008;452:375–379. - PubMed
-
- Bocquet N, et al. X-ray structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel in an apparently open conformation. Nature. 2009;457:111–114. - PubMed
-
- Jasti J, Furukawa H, Gonzales EB, Gouaux E. Structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1 at 1.9 A resolution and low pH. Nature. 2007;449:316–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

