Interleukin-23 production in dendritic cells is negatively regulated by protein phosphatase 2A
- PMID: 20404153
- PMCID: PMC2889593
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914703107
Interleukin-23 production in dendritic cells is negatively regulated by protein phosphatase 2A
Abstract
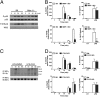
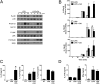
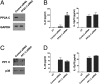
IL-12 and IL-23 are produced by activated antigen-presenting cells but the two induce distinct immune responses by promoting Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation, respectively. IL-23 is a heterodimeric cytokine consisting of two subunits: p40 that is shared with IL-12 and p19 unique to IL-23. In this study, we showed that the production of IL-23 but not IL-12 was negatively regulated by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) in dendritic cells (DC). PP2A inhibits IL-23 production by suppressing the expression of the IL-23p19 gene. Treating DC with okadaic acid that inhibits the PP2A activity or knocking down the catalytic subunit of PP2A with siRNA enhanced IL-23 but not IL-12 production. Unlike PP2A, MAP kinase phosphatase-1 or CYLD did not show an effect on IL-23 production supporting the specificity of PP2A. PP2A-mediated inhibition requires a newly made protein that is likely responsible for bringing PP2A and IKKbeta together upon LPS stimulation, which then results in the termination of IKK phosphorylation. Thus, our results uncovered an important role of the protein phosphatase in the regulation of IL-23 production and identified PP2A as a previously uncharacterized inhibitor of IL-23p19 expression in DC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
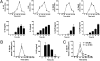
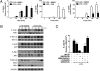
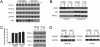

Similar articles
-
Cutting Edge: MMP-9 inhibits IL-23p19 expression in dendritic cells by targeting membrane stem cell factor affecting lung IL-17 response.J Immunol. 2014 Jun 15;192(12):5471-5475. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303183. Epub 2014 May 14. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24829419 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 negatively regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-23 p19 expression in human macrophages and dendritic cells and NF-kappaB p65 trans activation plays a novel role.J Immunol. 2006 Oct 1;177(7):4550-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4550. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16982892
-
Protein phosphatase 2A carboxymethylation and regulatory B subunits differentially regulate mast cell degranulation.Cell Signal. 2010 Dec;22(12):1882-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.07.017. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20688157
-
CCR7 ligands up-regulate IL-23 through PI3-kinase and NF-κ B pathway in dendritic cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Aug;92(2):309-18. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0811415. Epub 2012 May 16. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22591694
-
Protein Phosphatase 2A: Role in T Cells and Diseases.J Immunol Res. 2023 May 17;2023:4522053. doi: 10.1155/2023/4522053. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 37234102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of IFN-β on IL-12, IL-23, and IL-10 expression in TLR-stimulated dendritic cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2015 Nov;98(5):689-702. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3HI0914-453R. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26059829 Free PMC article.
-
Compound A Increases Cell Infiltration in Target Organs of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (aGVHD) in a Mouse Model.Molecules. 2021 Jul 12;26(14):4237. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144237. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299512 Free PMC article.
-
IL12B expression is sustained by a heterogenous population of myeloid lineages during tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2013 May;93(3):343-56. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2013.02.011. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2013. PMID: 23491716 Free PMC article.
-
Novel approach for interleukin-23 up-regulation in human dendritic cells and the impact on T helper type 17 generation.Immunology. 2011 Sep;134(1):60-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03467.x. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Immunology. 2011. PMID: 21718315 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in inflammation and neurodegeneration.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Sep;201:181-201. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.016. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31158394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kastelein RA, Hunter CA, Cua DJ. Discovery and biology of IL-23 and IL-27: Related but functionally distinct regulators of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:221–242. - PubMed
-
- Oppmann B, et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13:715–725. - PubMed
-
- Hunter CA. New IL-12-family members: IL-23 and IL-27, cytokines with divergent functions. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:521–531. - PubMed
-
- Smits HH, et al. Commensal Gram-negative bacteria prime human dendritic cells for enhanced IL-23 and IL-27 expression and enhanced Th1 development. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:1371–1380. - PubMed
-
- Sheibanie AF, Tadmori I, Jing H, Vassiliou E, Ganea D. Prostaglandin E2 induces IL-23 production in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. FASEB J. 2004;18:1318–1320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

