Transcription factor Late SV40 Factor (LSF) functions as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 20404171
- PMCID: PMC2889542
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1000374107
Transcription factor Late SV40 Factor (LSF) functions as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly aggressive cancer with no currently available effective treatment. Understanding of the molecular mechanism of HCC development and progression is imperative for developing novel, effective, and targeted therapies for this lethal disease. In this article, we document that the cellular transcription factor Late SV40 Factor (LSF) plays an important role in HCC pathogenesis. LSF protein was significantly overexpressed in human HCC cells compared to normal hepatocytes. In 109 HCC patients, LSF protein was overexpressed in >90% cases, compared to normal liver, and LSF expression level showed significant correlation with the stages and grades of the disease. Forced overexpression of LSF in less aggressive HCC cells resulted in highly aggressive, angiogenic, and multiorgan metastatic tumors in nude mice. Conversely, inhibition of LSF significantly abrogated growth and metastasis of highly aggressive HCC cells in nude mice. Microarray studies revealed that as a transcription factor, LSF modulated specific genes regulating invasion, angiogenesis, chemoresistance, and senescence. The expression of osteopontin (OPN), a gene regulating every step in tumor progression and metastasis, was robustly up-regulated by LSF. It was documented that LSF transcriptionally up-regulates OPN, and loss-of-function studies demonstrated that OPN plays an important role in mediating the oncogenic functions of LSF. Together, these data establish a regulatory role of LSF in cancer, particularly HCC pathogenesis, and validate LSF as a viable target for therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
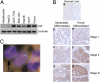
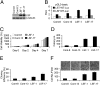
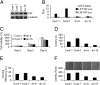
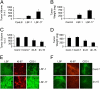



Similar articles
-
Antiproliferative small-molecule inhibitors of transcription factor LSF reveal oncogene addiction to LSF in hepatocellular carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 20;109(12):4503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121601109. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22396589 Free PMC article.
-
c-Met activation through a novel pathway involving osteopontin mediates oncogenesis by the transcription factor LSF.J Hepatol. 2011 Dec;55(6):1317-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.02.036. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21703197 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor LSF: a novel oncogene for hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2012;2(3):269-85. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Am J Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22679558 Free PMC article.
-
Late SV40 factor (LSF) enhances angiogenesis by transcriptionally up-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9).J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 27;287(5):3425-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.298976. Epub 2011 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22167195 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage-specific and ubiquitous biological roles of the mammalian transcription factor LSF.Gene. 2004 Dec 8;343(1):23-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.08.010. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15563829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Cell-Penetrant Peptide Disrupting the Transcription Factor CP2c Complexes Induces Cancer-Specific Synthetic Lethality.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Nov;10(33):e2305096. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305096. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37845006 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule inhibitors of Late SV40 Factor (LSF) abrogate hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Evaluation using an endogenous HCC model.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):26266-77. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4656. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26313006 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor LSF-DNMT1 complex dissociation by FQI1 leads to aberrant DNA methylation and gene expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):83627-83640. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13271. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27845898 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of miRISC Regulatory Network Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 25;23(19):11300. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911300. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232606 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative small-molecule inhibitors of transcription factor LSF reveal oncogene addiction to LSF in hepatocellular carcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 20;109(12):4503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121601109. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22396589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Sherman M Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42:1208–1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

