Preclinical model of organotypic culture for pharmacodynamic profiling of human tumors
- PMID: 20404174
- PMCID: PMC2889536
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907676107
Preclinical model of organotypic culture for pharmacodynamic profiling of human tumors
Abstract
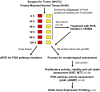
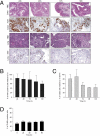
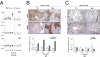
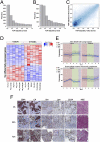
Predicting drug response in cancer patients remains a major challenge in the clinic. We have perfected an ex vivo, reproducible, rapid and personalized culture method to investigate antitumoral pharmacological properties that preserves the original cancer microenvironment. Response to signal transduction inhibitors in cancer is determined not only by properties of the drug target but also by mutations in other signaling molecules and the tumor microenvironment. As a proof of concept, we, therefore, focused on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, because it plays a prominent role in cancer and its activity is affected by epithelial-stromal interactions. Our results show that this culture model preserves tissue 3D architecture, cell viability, pathway activity, and global gene-expression profiles up to 5 days ex vivo. In addition, we show pathway modulation in tumor cells resulting from pharmacologic intervention in ex vivo culture. This technology may have a significant impact on patient selection for clinical trials and in predicting response to small-molecule inhibitor therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
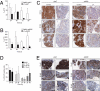
References
-
- Patocs A, et al. Breast-cancer stromal cells with TP53 mutations and nodal metastases. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2543–2551. - PubMed
-
- Orimo A, Weinberg RA. Stromal fibroblasts in cancer: A novel tumor-promoting cell type. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:1597–1601. - PubMed
-
- Peehl DM. Primary cell cultures as models of prostate cancer development. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:19–47. - PubMed
-
- Guyot C, Combe C, Clouzeau-Girard H, Moronvalle-Halley V, Desmoulière A. Specific activation of the different fibrogenic cells in rat cultured liver slices mimicking in vivo situations. Virchows Arch. 2007;450:503–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

