Plasmacytoid dendritic cells as guardians in hepatitis C virus-infected liver
- PMID: 20404186
- PMCID: PMC2867855
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002943107
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells as guardians in hepatitis C virus-infected liver
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
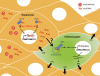
Comment on
-
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense hepatitis C virus-infected cells, produce interferon, and inhibit infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 20;107(16):7431-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002301107. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20231459 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Immunology of hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus infections.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;22(6):1049-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2008.11.015. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 19187866 Review.
-
Monitoring of Interferon Response Triggered by Cells Infected by Hepatitis C Virus or Other Viruses Upon Cell-Cell Contact.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1911:319-335. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8976-8_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30593636
-
Hepatitis C Virus Stimulates Murine CD8α-Like Dendritic Cells to Produce Type I Interferon in a TRIF-Dependent Manner.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Jul 6;12(7):e1005736. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005736. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27385030 Free PMC article.
-
IPS-1 is essential for type III IFN production by hepatocytes and dendritic cells in response to hepatitis C virus infection.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 15;192(6):2770-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301459. Epub 2014 Feb 14. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24532585
-
Intrahepatic natural immunity and HCV immunopathogenesis.Cell Death Differ. 2003 Jan;10 Suppl 1:S9-S12. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401116. Cell Death Differ. 2003. PMID: 12655338 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Co-Infection and Cancer: Host-Pathogen Interaction between Dendritic Cells and HIV-1, HTLV-1, and Other Oncogenic Viruses.Viruses. 2022 Sep 14;14(9):2037. doi: 10.3390/v14092037. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relative Expression of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 7 mRNA in Peripheral Blood of Patients With Hepatitis C.Hepat Mon. 2015 Nov 28;15(11):e30427. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.30427. eCollection 2015 Nov. Hepat Mon. 2015. PMID: 26834788 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging concepts in immunity to hepatitis C virus infection.J Clin Invest. 2013 Oct;123(10):4121-30. doi: 10.1172/JCI67714. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 24084744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

