(-)-epicatechin activation of endothelial cell endothelial nitric oxide synthase, nitric oxide, and related signaling pathways
- PMID: 20404222
- PMCID: PMC2874202
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.147892
(-)-epicatechin activation of endothelial cell endothelial nitric oxide synthase, nitric oxide, and related signaling pathways
Abstract
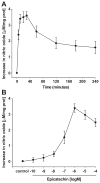
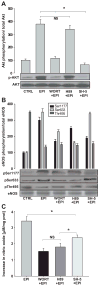
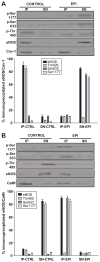
Recent reports indicate that (-)-epicatechin can exert cardioprotective actions, which may involve endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-mediated nitric oxide production in endothelial cells. However, the mechanism by which (-)-epicatechin activates eNOS remains unclear. In this study, we proposed to identify the intracellular pathways involved in (-)-epicatechin-induced effects on eNOS, using human coronary artery endothelial cells in culture. Treatment of cells with (-)-epicatechin led to time- and dose-dependent effects that peaked at 10 minutes at 1 mumol/L. (-)-Epicatechin treatment activates eNOS via serine 633 and serine 1177 phosphorylation and threonine 495 dephosphorylation. Using specific inhibitors, we have established the participation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in eNOS activation. (-)-Epicatechin induces eNOS uncoupling from caveolin-1 and its association with calmodulin-1, suggesting the involvement of intracellular calcium. These results allowed us to propose that (-)-epicatechin effects may be dependent on actions exerted at the cell membrane level. To test this hypothesis, cells were treated with the phospholipase C inhibitor U73122, which blocked (-)-epicatechin-induced eNOS activation. We also demonstrated inositol phosphate accumulation in (-)-epicatechin-treated cells. The inhibitory effects of the preincubation of cells with the calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitor KN-93 indicate that (-)-epicatechin-induced eNOS activation is at least partially mediated via the Ca(2+)/CaMKII pathway. The (-)-epicatechin stereoisomer catechin was only partially able to stimulate nitric oxide production in cells. Together, these results strongly suggest the presence of a cell surface acceptor-effector for the cacao flavanol (-)-epicatechin, which may mediate its cardiovascular effects.
Figures





Similar articles
-
(-)-Epicatechin induces calcium and translocation independent eNOS activation in arterial endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Apr;300(4):C880-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00406.2010. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21209365 Free PMC article.
-
Propionyl-L-carnitine induces eNOS activation and nitric oxide synthesis in endothelial cells via PI3 and Akt kinases.Vascul Pharmacol. 2013 Sep-Oct;59(3-4):76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Vascul Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23850990
-
Far-infrared radiation acutely increases nitric oxide production by increasing Ca(2+) mobilization and Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase at serine 1179.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jul 12;436(4):601-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.06.003. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23756809
-
Phosphorylation of Thr(495) regulates Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity.Circ Res. 2001 Jun 8;88(11):E68-75. doi: 10.1161/hh1101.092677. Circ Res. 2001. PMID: 11397791
-
Beneficial effect of the oligomerized polyphenol oligonol on high glucose-induced changes in eNOS phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Feb;159(4):928-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00594.x. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20128797 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cocoa Flavanols Improve Vascular Responses to Acute Mental Stress in Young Healthy Adults.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 27;13(4):1103. doi: 10.3390/nu13041103. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33801767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Syringaresinol causes vasorelaxation by elevating nitric oxide production through the phosphorylation and dimerization of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.Exp Mol Med. 2012 Mar 31;44(3):191-201. doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.3.014. Exp Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22170035 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Epicatechin Is a Biased Ligand of Apelin Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 11;23(16):8962. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168962. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012227 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent increases in flow-mediated dilation following acute cocoa ingestion in healthy older adults.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011 Dec;111(6):1568-74. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00865.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 8. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011. PMID: 21903881 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intravenous (-)-epicatechin reduces myocardial ischemic injury by protecting mitochondrial function.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Aug 1;175(2):297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.05.009. Epub 2014 May 15. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24908200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Räthel TR, Samtleben R, Vollmar AM, Dirsch VM. Activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by red wine polyphenols: impact of grape cultivars, growing area and the vinification process. J Hypertens. 2007;25:541–549. - PubMed
-
- O’Riordan E, Chen J, Brodsky SV, Smirnova I, Li H, Goligorsky MS. Endothelial cell dysfunction: the syndrome in making. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1654–1658. - PubMed
-
- Napoli C, Ignarro LJ. Nitric oxide and pathogenic mechanisms involved in the development of vascular diseases. Arch Pharm Res. 2009;32:1103–1108. - PubMed
-
- Corti R, Flammer AJ, Hollenberg NK, Lüscher TF. Cocoa and cardiovascular health. Circulation. 2009;119:1433–1441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

