Mzm1 influences a labile pool of mitochondrial zinc important for respiratory function
- PMID: 20404342
- PMCID: PMC2885224
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.109793
Mzm1 influences a labile pool of mitochondrial zinc important for respiratory function
Abstract
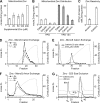
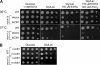
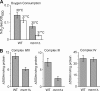
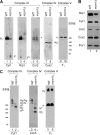
Zinc is essential for function of mitochondria as a cofactor for several matrix zinc metalloproteins. We demonstrate that a labile cationic zinc component of low molecular mass exists in the yeast mitochondrial matrix. This zinc pool is homeostatically regulated in response to the cellular zinc status. This pool of zinc is functionally important because matrix targeting of a cytosolic zinc-binding protein reduces the level of labile zinc and interferes with mitochondrial respiratory function. We identified a series of proteins that modulate the matrix zinc pool, one of which is a novel conserved mitochondrial protein designated Mzm1. Mutant mzm1Delta cells have reduced total and labile mitochondrial zinc, and these cells are hypersensitive to perturbations of the labile pool. In addition, mzm1Delta cells have a destabilized cytochrome c reductase (Complex III) without any effects on Complexes IV or V. Thus, we have established that a link exists between Complex III integrity and the labile mitochondrial zinc pool.
Figures




References
-
- Coyne H. J., 3rd, Ciofi-Baffoni S., Banci L., Bertini I., Zhang L., George G. N., Winge D. R. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 8926–8934 - PubMed
-
- Eide D. J. (2006) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1763, 711–722 - PubMed
-
- Jackson K. A., Helston R. M., McKay J. A., O'Neill E. D., Mathers J. C., Ford D. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 10423–10431 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

