Cohesins coordinate gene transcriptions of related function within Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 20404480
- PMCID: PMC3096706
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.9.8.11307
Cohesins coordinate gene transcriptions of related function within Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
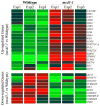
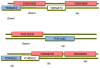
Cohesion factors pair together sister chromatids from early S-phase until anaphase onset. Numerous findings also establish an additional role in transcription. In humans, mutations in cohesion factors result in developmental abnormalities such as Cornelia de Lange, Roberts Syndrome/SC-Phocomelia, Rothman-Thompson Syndrome and others. While clinically relevant, a detailed study that links experimentally-defined cohesin defects to transcriptional changes remains lacking. Here, we report on the effects of cohesin inactivation during an early and discrete portion of the cell cycle. Even transient cohesin inactivation during the G1 portion of the cell cycle results in significant and reproducible changes in transcription. Surprisingly, over a third of the affected genes exhibit inter-related functions, suggesting that cohesin positioning along chromosomes evolved to coordinate gene expression. Prior studies indicate that defects in rRNA maturation/ribosome biogenesis produce developmental maladies in humans. Thus, the identification of genes critical for rRNA maturation in this study is of particular interest.
Figures
References
-
- Skibbens RV. Mechanisms of sister chromatid pairing. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2009;269:283–339. - PubMed
-
- Unal E, Heidinger-Pauli JM, Kim W, Guacci V, Onn I, Gygi SP, Koshland DE. A molecular determinant for the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion. Science. 2008;321:566–569. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shahar TR, Heeger S, Lehane C, East P, Flynn H, Skehel M, et al. Eco1-dependent cohesin acetylation during establishment of sister chromatid cohesion. Science. 2008;321:563–566. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Shi X, Li Y, Kim BJ, Jia J, Huang Z, et al. Acetylation of Smc3 by Eco1 is required for S phase sister chromatid cohesion in both human and yeast. Mol Cell. 2008;31:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Sutani T, Kawaguchi T, Kanno R, Itoh T, Shirahige K. Budding yeast Wpl1(Rad61)-Pds5 complex counteracts sister chromatid cohesion-establishing reaction. Curr Biol. 2009;24:492–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
